What Is Business Process Automation? Use Cases, Best Practices, and How to Implement It in Your Organization
As a business owner, you know that repetitive tasks like order processing, approvals, call handling, message responses, and so on, are essential parts of daily operations. You may also know that doing these tasks manually can result in major pain as mistakes made by humans tend to multiply and create chaos.
Thankfully, there is a more efficient way to deal with these routine duties. Automation of business procedures will help you save time, cut down on errors, and concentrate on expanding your business.
As a software development and IT consulting company, at Flyaps, we worked with many businesses, helping them automate their routine tasks. We apply robotic process automation (RPA), artificial intelligence, AI development platforms and low-code platforms to help our clients speed up their operations, increase employee productivity and ultimately improve the bottom line.
In the following paragraphs, we will share our expertise in business process automation (BPA), along with practical guidance and industry-specific examples. So, keep reading to discover how BPA can benefit your business.
What is business process automation (BPA)?
Let’s start with the definition. Simply put, BPA is about using technology to streamline repetitive tasks to improve a company’s performance. Examples of where BPA is typically implemented include customer support, marketing, HR, sales, and more.
Thanks to BPA, you don't only minimize the number of potential errors, but also get analytical insights to help you define how to improve your business processes further. Let's look more into the benefits of BPA.
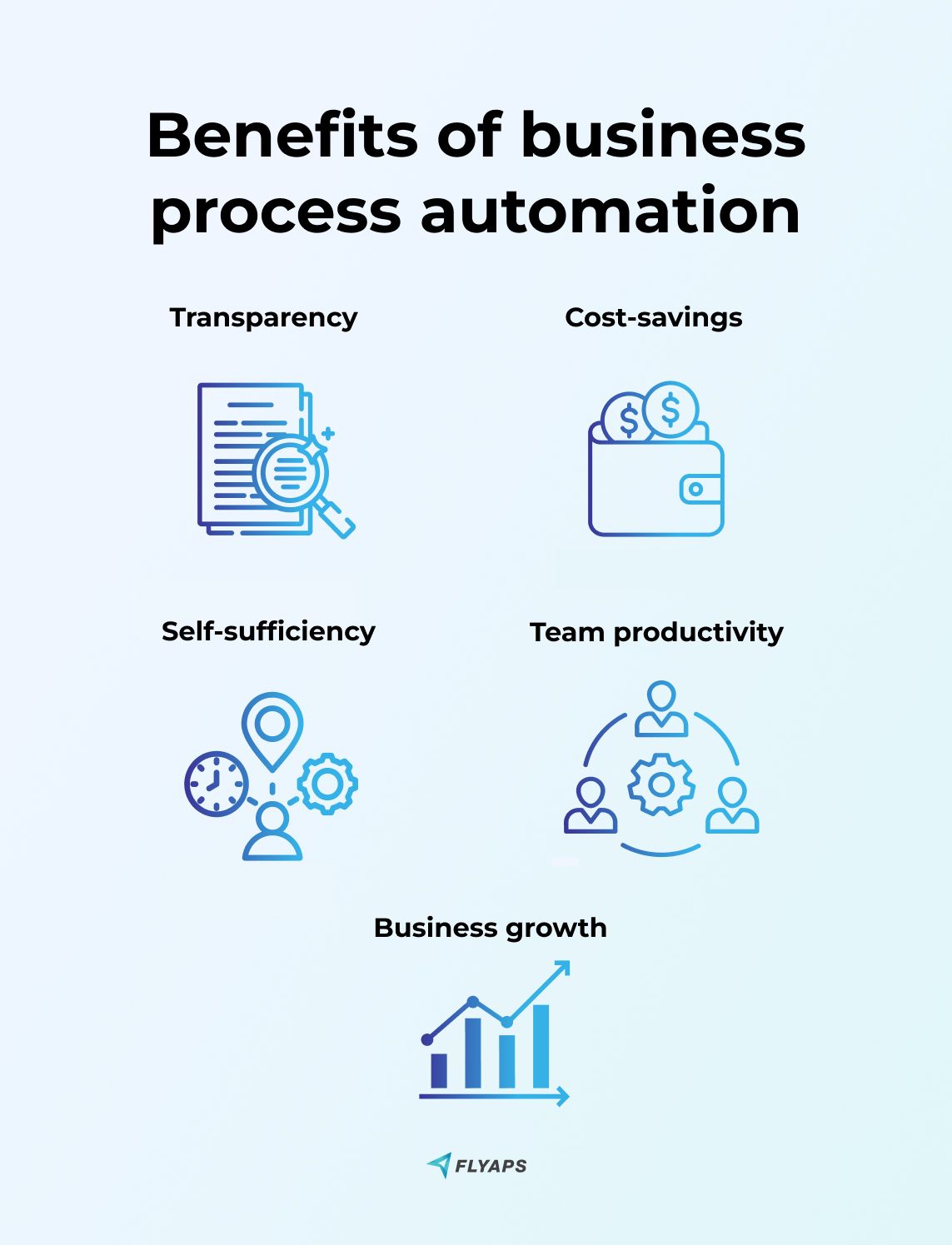
- Transparency: BPA gives you a clear picture of the whole business process by collecting data from its different stages. For example, with BPA software, you can track the manufacturing process from initial order to delivery. By tracking, monitoring, and providing analytics on these steps, BPA will help you identify bottlenecks and see potential areas for improvements.
- Cost-savings: By implementing BPA, you can reduce the expenses associated with manual labor and minimize delays and errors. This results in faster turnaround times, which saves both time and money. The cost savings can then be reinvested into the business to enhance its competitiveness in the market.
- Self-sufficiency: By automating repetitive tasks, your business can become more self-sufficient as you won’t have to rely on any third party to help you optimize your workload.
- Team productivity: BPA allows teams to shift their attention towards higher-value work where they can apply their expertise and skills more effectively. Also, they can undertake more challenging and fulfilling tasks that increase their morale and productivity.
- Business growth: When the requirement for manual labor decreases, it results in significant savings on salaries, benefits, and other related costs. These funds can be put in other areas of the business, such as research and development, marketing, or customer service, to facilitate the business's faster growth.
Now that we’ve talked about some exciting benefits BPA can bring to the table, let's look at some of the fun things happening in business process automation, with a focus on robotic process automation (RPA) and the use of artificial intelligence.
What is robotic process automation (RPA)?
Imagine having a robot that can mimic your actions and do all the repetitive tasks for you. Sounds like a dream, right? In a nutshell, that’s what RPA is. It takes care of all the boring work like entering data, invoice processing, making calculations and so on. You may ask, how does it differ from BPA then? A great question, so let’s talk about it more.
Business process automation vs. robotic process automation
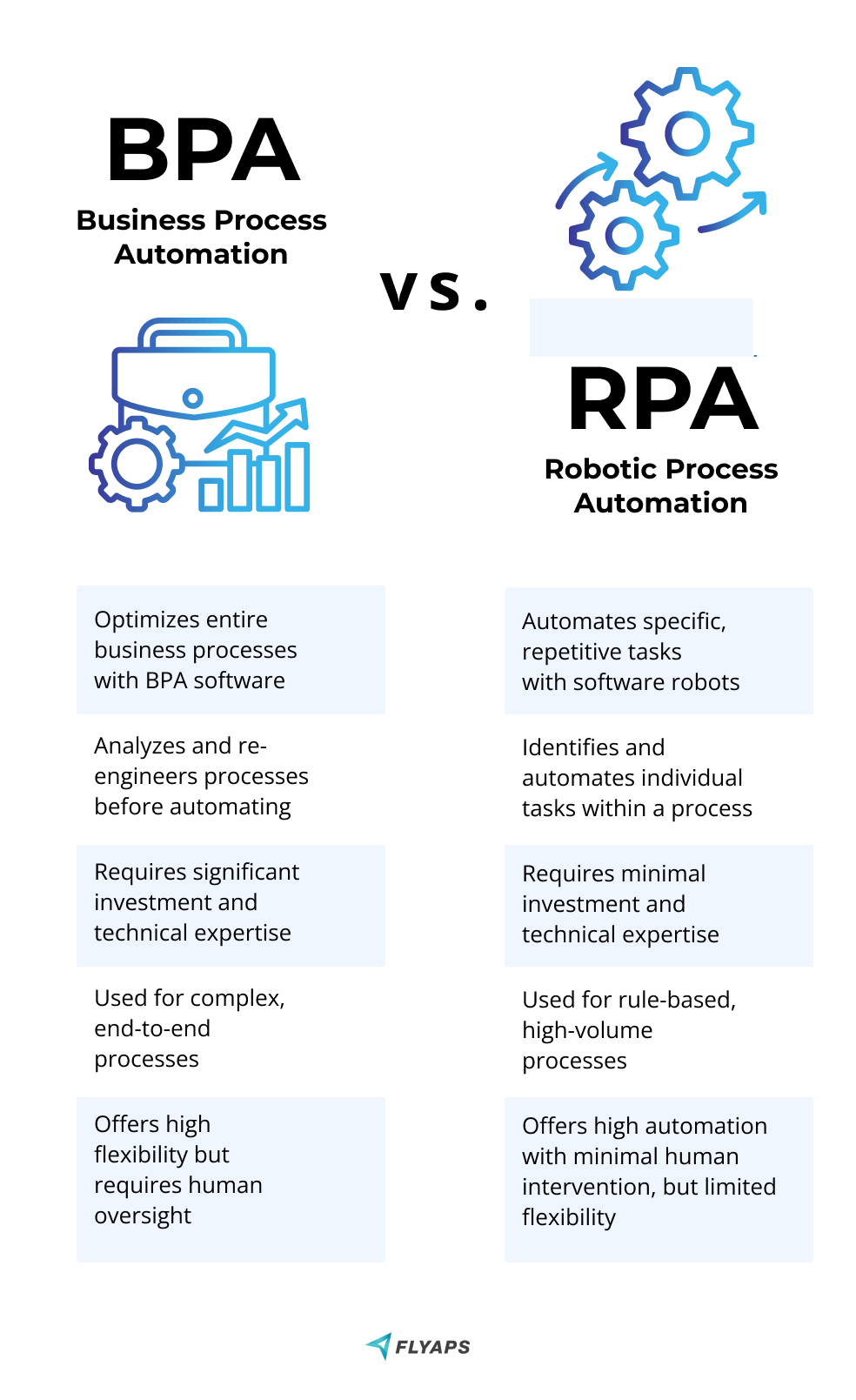
RPA and BPA are the main methods for automating business operations. They are similar yet distinct.
BPA is a type of software that automates complex end-to-end business processes through the use of predefined business rules. These processes typically involve multiple systems, such as order processing or inventory management, and require human decision-making and judgment. On the other hand, RPA is a type of software that automates repetitive and rule-based tasks. It uses bots to mimic human actions, such as entering data into forms or copying and pasting information between systems.
Long story short, BPA streamlines complex business processes and RPA automates repetitive rule-based tasks.
Now, let's focus on how AI can be used to help you optimize business processes.
If you’re thinking about integrating AI into your operations, be sure to explore our guide on AI implementation strategies to learn how to approach it effectively and avoid common pitfalls.
The use of AI in business process automation
AI and machine learning (ML) allow BPA and RPA to improve over time by allowing automation to learn from data. Exciting, right? Many ready-made RPAs solutions employ AI and ML to ensure a better user experience and make the tool “learn on the go.” Here are a few more ways in which AI and machine learning can be used:
- Predictive analytics: AI and ML allow organizations to look past data to predict future events and spot potential problems before they even appear. For example, if you run an online store, AI can help you forecast which products are likely to gain popularity during a particular season, enabling you to adjust your inventory levels and ensure that you neither have an excess nor a shortage of items.
- Natural language processing: NLP is a technology behind chatbots that allows them to mimic human-like conversations. Everybody knows about OpenAI’s ChatGPT, but did you know that NLP can also be used to determine sentiment behind a piece of text such as a customer review or social media post, convert spoken language into text, extract information about specific entities mentioned in text, such as people or organizations, etc. There are many use cases for NLP beyond just chatbots.
- Intelligent automation: Also called cognitive automation, IA is about using AI, RPA, and business process management (BPM) to help organizations make better decisions, simplify processes, save resources, and make things run more smoothly. There are lots of ways that intelligent automation can be useful like in the healthcare industry it can help analyze data, diagnose problems, and figure out treatments. These are just a few examples of how generative AI is reshaping operations across industries. To explore more real-world applications, check out our article on Generative AI use cases.
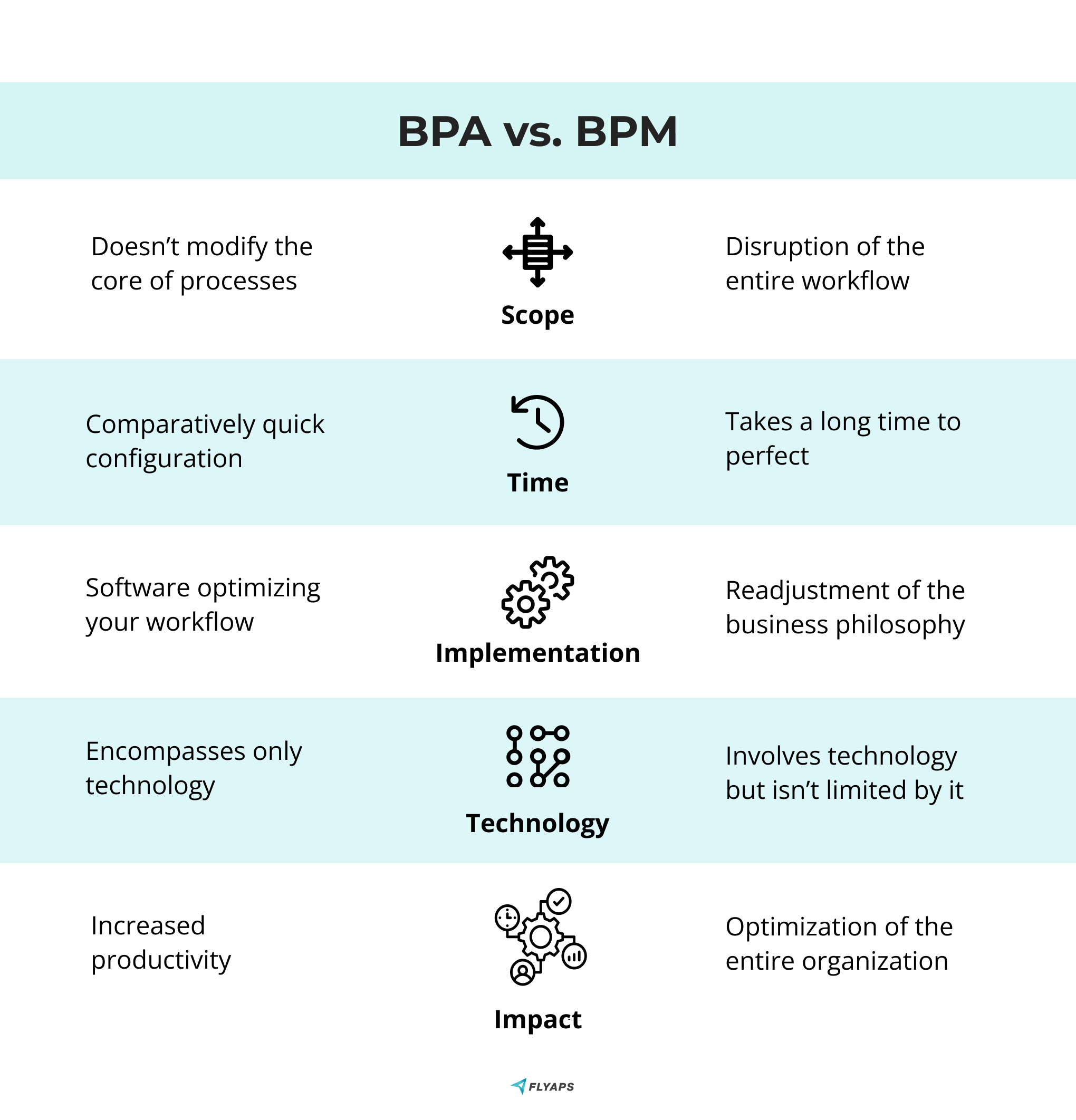
Before we jump to the BPA use cases, let’s clear up the last thing which is Business Process Management (BPM), a term often confused with BPA. Let’s see how they are different.
How is BPA different from business process management (BPM)?
BPM is about analyzing, designing, implementing, and continuously improving business processes. It’s all about getting your business running like an engine, which might involve giving it a complete makeover.
BPA handles all the nitty-gritty tasks, especially the boring ones like data entry, invoice processing, and building reports – you know. The tasks you won’t mind bots handling for you on autopilot.
In one sentence, BPA is a powerful tool that can be used as part of a BPM strategy.
Use cases of BPA
The possibilities for BPA are endless, from streamlining employee onboarding process to optimizing a sales funnel. Let's look at some examples of how BPA can be used to enhance business outcomes.
Telecom
BPA is widely used in the telecom industry to automate customer service, improve billing accuracy, and service provisioning.
For instance, Flyaps has been collaborating with NetSpark IP & Telecom, a telecommunications consulting firm based in Texas that provides services from AT&T. As their business grew, the company realized that their manual work processes were slowing down project delivery, so they needed more tools to keep up. They decided to partner with Flyaps to implement a BPA solution.
We helped NetSpark IP & Telecom develop a custom CRM/ERP application that centralized project management and client connections in a single location and an RPA tool that helps find the right combination of AT&T tariff plans for each client.
As a result, our client achieved smoother project implementation, improved team performance, and increased revenue. You can read more about it in our full case study.
HR & Recruitment
Luckily, the days of spending countless hours manually reviewing each resume and application form are over. Today, most of the recruitment process – from sourcing and screening to employee onboarding – can be automated.
Let me give you an example. GlossaryTech, an HR technology startup, needed help developing a CV analysis algorithm for their product, CV Compiler. To automate the process of candidate screening, our team at Flyaps built a resume-checking tool that looks into word counts, page numbers, creates summaries, and more for their product.
Our collaboration continues today to further improve the product and ensure a more streamlined workflow for our client.
Customer service
BPA has many applications in customer service, including the automation of tasks such as customer data collection, ticket routing, and follow-up communications. By automating these processes, customer service agents can prioritize more complex and pressing issues, resulting in faster resolution times and increased customer satisfaction.
Deploying an NLP chatbot, as recommended by IBM, can further enhance the customer experience and lead to more sales while also reducing customer support costs by up to 30%.
Marketing
From scheduling posts for social media to segmenting customers based on demographics, behavior, or preferences, BPA has many use cases in marketing. Some of the most common marketing tasks that can get automated include lead scoring, email campaign management, content creation, data collection and analysis, lead tracking, and others.
Sales
Sales teams can gain a lot from business process automation, too. By automating tasks such as lead generation, lead nurturing, and sales forecasting, sales representatives can focus more on closing deals and building stronger relationships with customers.

How to implement BPA?
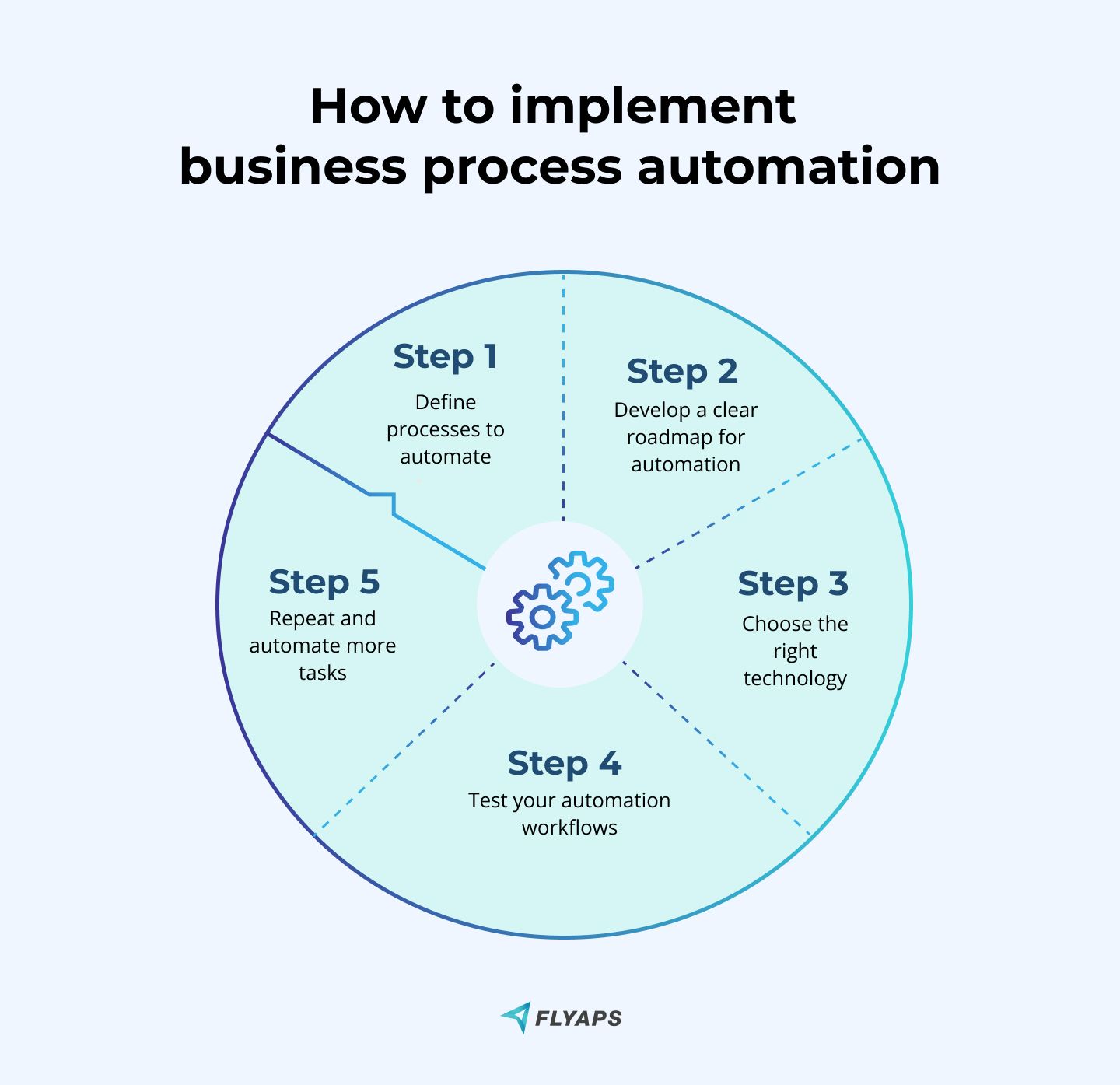
Using BPA might seem overwhelming at first, but if done right, it can lead to significant rewards. By cutting labor costs and reducing errors with BPA, you can save a lot of money and increase efficiency. To get rid of boring manual tasks and get more efficient workflows, just follow these steps:
Step 1: Define processes to automate
Take a close look at your current business processes and identify any tasks that are repetitive, time-consuming, and prone to errors when done manually. These are the tasks that are best suited for automation.
However, it's important to note that processes that require creative thinking, problem-solving skills, emotional intelligence, and a human touch should be left to human workers, as they are difficult to automate with current technology.
Step 2: Develop a clear plan and roadmap for automation
Before automating anything, map out these processes step-by-step and briefly describe each procedure and person involved. It's best to draw the process using business process flow diagrams to see all the dependencies, roles, and other factors.
Step 3: Choose the right technology
Companies can use pre-built RPA tools like UiPath to automate business processes in various departments such as customer service and finance. For tasks like email marketing, Mailchimp is a popular choice, and BambooHR or Zenefits are effective for automating HR processes such as candidate sourcing, screening, and scheduling.
Step 4: Test your automation workflows
Testing is essential to ensure that automation delivers the best results and functions correctly. The testing process involves:
- Identifying scenarios to be tested.
- Preparing test data that will be used to test the workflows. This may include creating test user accounts, sample orders, or any other relevant data.
- Conducting testing to ensure that the workflows behave as expected. This can include testing the user interface, validating the output, and confirming the workflow logic.
- Recording test results and defining what could be improved.
Let’s say you want to automate consumer order processing. Processes like customer orders, inventory checks, invoices, and delivery are going to be automated.
First of all, you need data on customer orders, inventory, and prices to test this automated process. Then you must design test scenarios that imitate situations, for example, a consumer ordering an out-of-stock product or asking for a refund. These scenarios allow you to uncover automation issues like inventory level mismatches, invoice generating errors, and customer invoice delays. This data can then be used to improve the automated process.
Before implementing a BPA solution throughout the organization, thoroughly test it to ensure it functions as intended.
Step 5: Once done, look for more tasks to automate
Over time, you'll start to notice more tasks that can be automated. When you feel like another business operation can be optimized, come back to step one and repeat the process all over again, while keeping an eye out for fresh opportunities for automation.
Automate your business processes with Flyaps
Automating your business processes can bring various benefits, from increased efficiency and accuracy to improved customer satisfaction. However, not all off-the-shelf BPA tools available can be right for your unique business needs and sometimes you might require a custom solution.
Flyaps can help you out. Our team specializes in creating tailored automation solutions that fit the specific requirements of our clients. Drop us a line if you need help building a tailored automation solution.






