Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Artificial Intelligence (AI): Exploring How Intelligent Technologies Can Solve Problems in Business

Imagine three companies. The first company doesn’t employ any automation solutions and performs all tasks manually. The second company uses RPA to streamline certain tasks, while the third company combines RPA with AI. Which one do you think will perform better in the long run?
The first company will definitely lag behind, as it will have to spend plenty of time doing everything manually with a constant risk of human error. The second company will perform better, but as RPAs only allow to automate specific tasks and nothing but them, the business would still have some room for improvement.
So yes, the clear winner here is a third company. Why? It is all thanks to this perfect mix of RPA+AI. When combined, RPA and AI drive intelligent automation that allows to get rid of human errors, while reducing costs and saving employees’ time and nerves.
With more than a decade of experience in helping companies automate their business processes and building custom solutions, we at Flyaps are confident that the future is behind robotic process automation and the use of AI-driven solutions. More and more companies reach out to us, looking to streamline repetitive tasks using the power of the latest technology, especially in the telecom industry, where many processes still depend on manual labor.
In this blog post, we will discuss the difference between RPA and AI and how they can be used for business process automation. We will also talk about how you can combine both, so keep reading to learn more.
How does RPA work?
To better understand how RPA can be applied to optimize business processes, let’s take an example of a finance department in a large company. Normally, finance departments receive hundreds of invoices every day from various vendors, and dealing with all those invoices manually is a challenging job, which often leads to occasional mistakes and employee burnout. According to recent reports of Wax Digital, 82% of finance departments state they are overwhelmed with the number of invoices they should process on a daily basis.
This is when the RPA solution can be applied to automate invoice reviewing. Here's how it works:
- Data extraction: The bot extracts the relevant data from the invoices, such as vendor name, invoice number, date, and amount. This can be done using Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology, which can read text from scanned images and PDF files.
- Validation: Once the data is extracted, the bot validates it against pre-defined rules to ensure that it is accurate and complete. For example, the bot can check if the vendor name and invoice number match the records in the company's database.
- Processing: Once the data is validated, the RPA bot automatically enters it into the company's accounting system and generates payment instructions for the finance team to review and approve.
- Reporting: Finally, the bot can generate reports on the invoice processing activity, providing insights into the number of invoices processed, the average processing time, and any errors or exceptions that occurred.
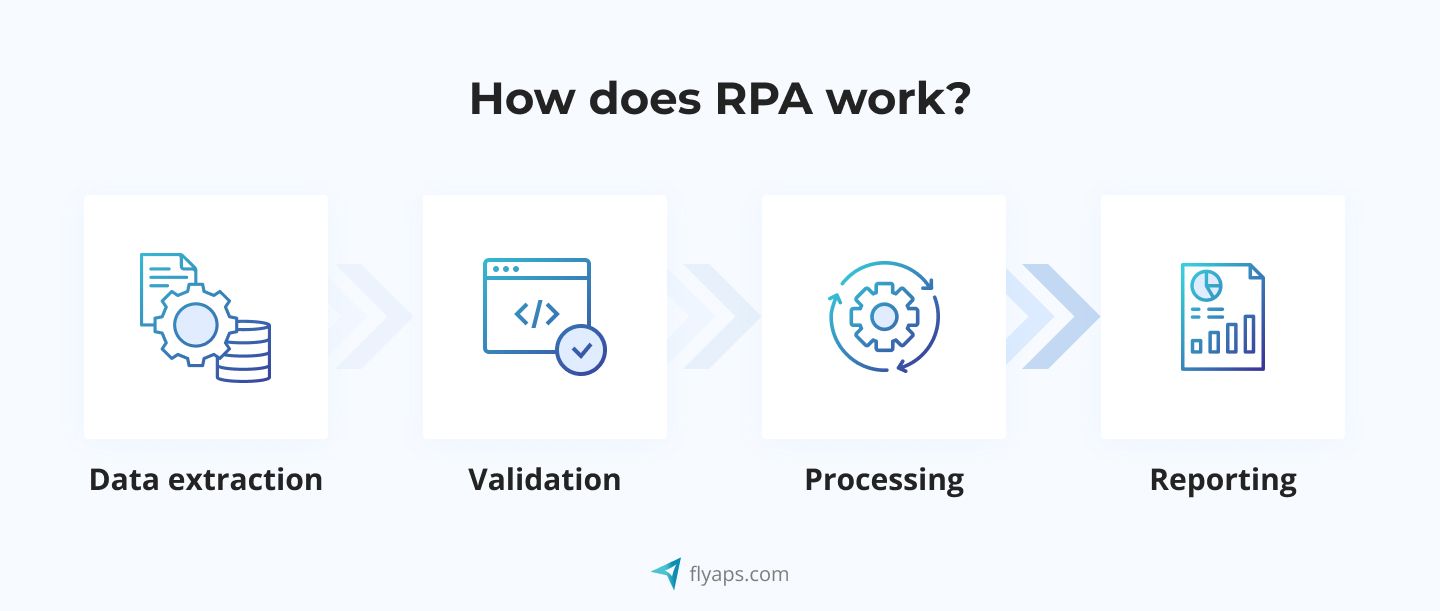
By using RPA in our scenario, the finance team can streamline their workflow, reducing the number of errors, and improving efficiency. What’s more, unlike humans, the bot can work 24/7 without getting tired, processing invoices much faster than a human worker, and freeing up the finance team's time for more strategic tasks in the end.
Sure thing, robotic process automation does magic in our case. But can we make it work even better?
AI can do more for your business—let’s find the best way to make it work for you. Check out our expertise and let’s discuss your next AI project.
See out AI services
RPA and AI. How using AI can take robotic process automation further
While RPA solutions come as lifesavers in many AI use cases, they still pose certain limitations. For example, RPA solutions can only work with structured data, which means they can’t be of great help when working with images, graphs, PDF documents, and so on. Also, designed to automate repetitive and rule-based tasks, RPA solutions can’t perform tasks requiring reasoning, decision-making, and creativity. Last but not least, the RPA solutions can only perform tasks they were programmed to do, and any changes in the workflow may require significant reprogramming.
So, is there a way to enhance RPA solutions and make your business process automation more intelligent? In fact, yes, and this is where we should mention AI.
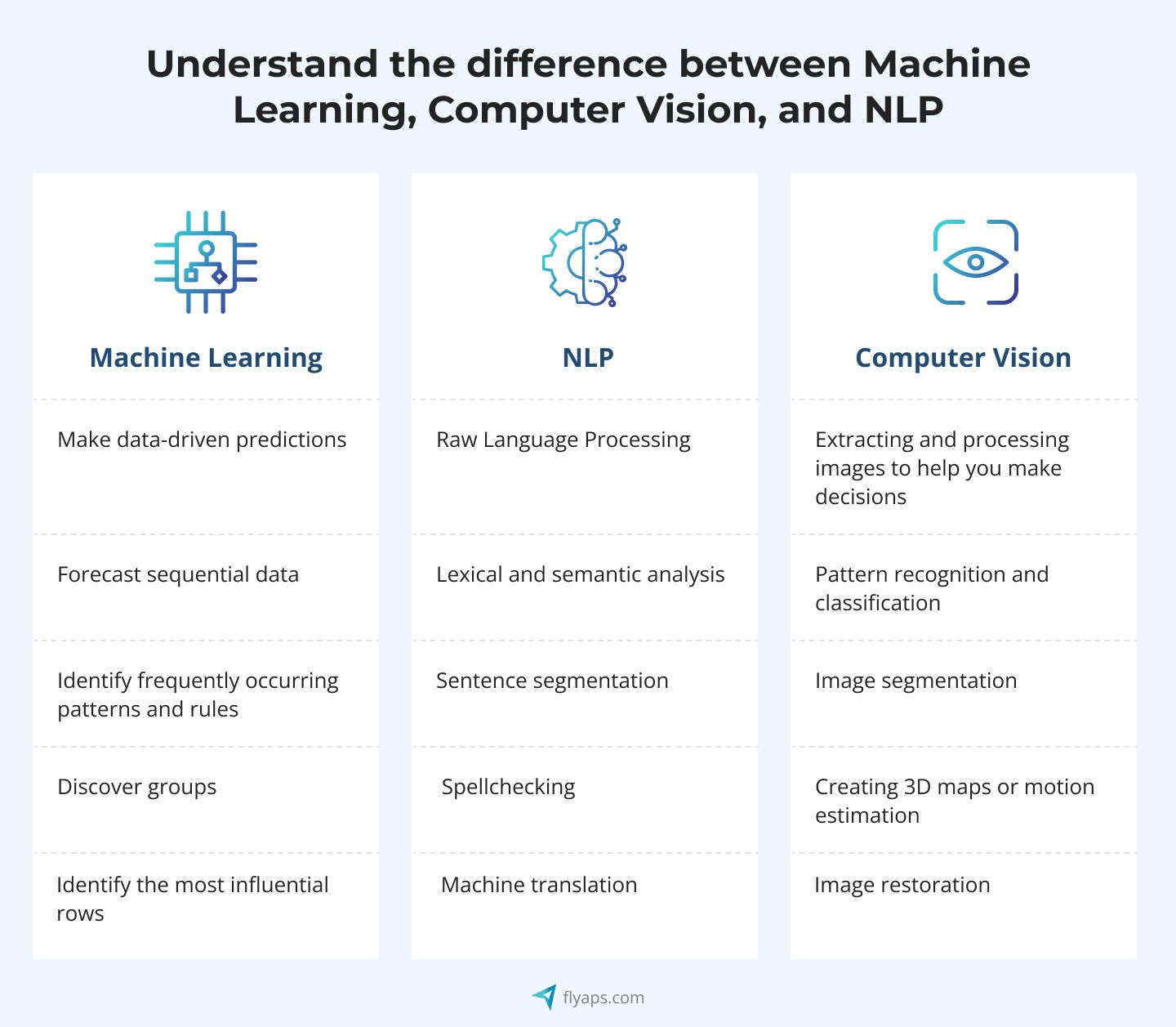
AI is a technology that enables machines to learn from specific datasets and make decisions in a human-like manner. It encompasses a wide range of techniques, including machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and computer vision. AI can be used to automate tasks that require human intelligence, such as, for example, recognizing patterns, making predictions, and text analysis.
RPA and AI are often combined to automate complex tasks that require both rule-based and intelligent decision-making. For better understanding, let’s circle back to our finance department example and see how artificial intelligence (AI) can be used to enhance the existing RPA system:
- Intelligent document understanding: AI can be used to improve the accuracy of data extraction by understanding the meaning and context of the invoice data rather than simply relying on OCR technology. This can help to reduce errors and exceptions in the invoice processing workflow.
- Decision-making: AI can be used to make intelligent decisions based on the data extracted from the invoices. For example, the system can detect unusual patterns in the data and flag them for human review, or it can automatically approve invoices that meet specific criteria.
- Natural language processing: AI can be used to understand and interpret natural language inputs, such as email inquiries from vendors, and generate appropriate responses. This can reduce the workload of the finance team and improve customer service.
- Predictive analytics: AI can be used to analyze invoice data over time and identify trends and patterns to shape future decision-making. For example, the system can predict which vendors are likely to provide the best discounts or identify potential fraud or error in the invoice data.
Overall, by incorporating AI into the RPA system, our hypothetical finance department can further streamline its invoice processing workflow and improve accuracy, and decision-making. Sounds great, if you ask us!
But here’s the question: how can you combine AI and RPA, so that it works efficiently? We’re just about to answer this question.
Read also: Three Key Trends in Business Process Automation
How to implement AI in RPA?
Though it sounds very easy to “add AI” in the RPA system and call it a day, it is a complex process that involves the following steps.
- Define the problem: The first step in implementing AI in RPA is to define the problem you want to solve. Depending on your needs, it could be anything, from invoice processing to improving customer support services.
- Collect data: Once you have defined the problem, you need to collect data that can be used to train an AI algorithm. Again, it all comes down to the process you’re about to automate. For example, when you’re about to streamline operations related to customer service, you should collect customer feedback and data related to customer support operations (for instance, phone support or email support).
- Train the AI model: Once you have collected the data, use it to train an AI model. This will involve selecting an appropriate algorithm. For example, when you have a labeled dataset that you want the AI model to learn from, you can use supervised learning algorithms. These algorithms are commonly used in tasks such as image recognition, speech recognition, and natural language processing.
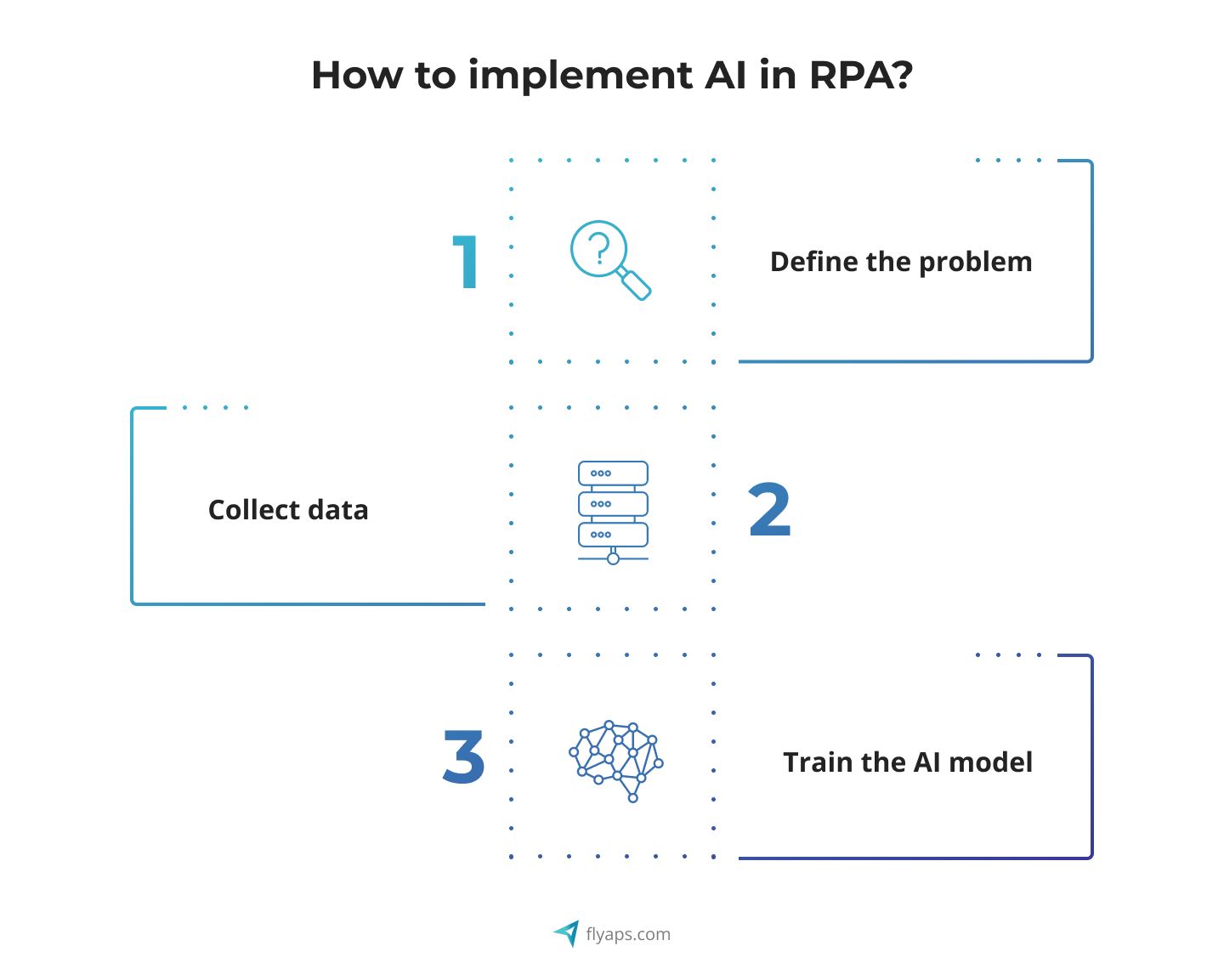
With the data and algorithm in place, it's time to train the AI model. This involves “feeding” the labeled data into the algorithm and adjusting the model's parameters until it accurately predicts the desired output. Once the model is trained, it's important to test it on new, unlabeled data to ensure that it can adapt to new unfamiliar situations. You may need to refine the model and adjust its parameters later on based on the results of these tests.
- Integrate the AI model with RPA: Once your AI model is trained on the collected data, it’s time to integrate it with your RPA solution. This could involve using an application programming interface (API) or building custom connectors to enable the RPA solution to interact with the AI model, so make sure you have developers with relevant expertise on board to make it happen.
- Test and deploy: Once you have integrated the AI model with RPA, your development team will need to test the solution to ensure that it is working correctly.
And there’s that, your RPA is now AI-powered, congratulations! We wish we could have said that and end the story here, but there’s some more to add. As we briefly mentioned, AI includes different branches, like computer vision, NLP, and ML. Depending on your project, you will want to integrate a different solution, so that’s why, let’s talk a bit more about them.
Ways how different branches of AI can be applied to RPA
Below are the main branches that could be applied to RPA solutions, improving their efficiency and accuracy further.
Computer vision: A smart bot that sees and understands everything like humans
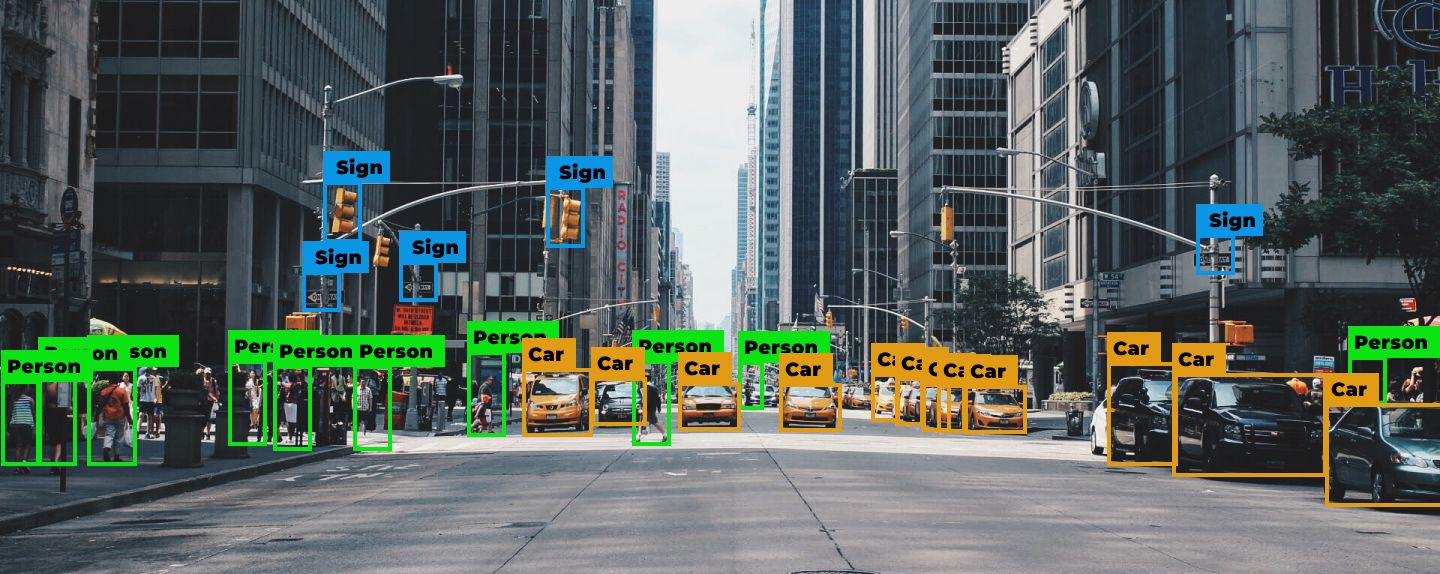

Computer vision is a field of AI that handles image and video analysis. The technology also includes the use of a photo or video camera to replicate a human-like vision that extracts information from the visual world. Lastly, it involves using specialized software to identify and classify objects from unstructured data. Computer vision rests on two pillars: deep learning and a convolutional neural network. These two technologies are highly important to learn context through visual data analysis.
Let’s say you have a warehouse to store goods. Some items are delivered daily, and some on a weekly basis. Arranging goods can turn into a time-consuming process that is making your workers perform tedious and monotonous tasks, and let’s not even imagine when you have several warehouses. As an outcome, your employees will have to spend hours and hours of their time arranging all the goods, while not forgetting where each particular type of goods is stored.
A robotic process automation equipped with computer vision can detect all the goods in mere seconds and keep count of all of them, taking the burden off your employees’ shoulders. What’s more, by scanning each product, the RPA solution can provide each item with an attributed class to automate the process of arranging goods in the warehouse. So instead of verifying each parcel manually, your workers can focus on more demanding, higher-value tasks.
Machine learning + RPA = unlimited possibilities
ML is a branch of AI that is at the core of many approaches to AI. With ML, your software solution can analyze, compare, and structure data. Here’s an example for better understanding. Imagine that while constantly learning and improving accuracy thanks to specific algorithms. Simply put, ML allows RPA solutions to learn from historical data and improve over time.
t you are running a hot strip steel mill and you need to define the right chemical composition to keep production running. It takes a lot of resources to find out the chemical composition for industry-scale production, and chemical compositions are a large operational cost item. Any mistake can be expensive.
In this case, you can use historical data to teach the ML-driven solution how to make a required chemical composition in different ways and optimize your work process, as a result. What’s more, ML-powered RPA can provide insights into how each approach would influence other chemical processes in your enterprise, which will help improve the overall efficiency of your business.
Smart automation with NLP: an RPA solution that understands human language
At its core, NLP is about creating software and algorithms that can process and analyze human language in a way that is useful for various applications. This includes tasks like language translation, text summarization, sentiment analysis, and speech recognition, to name a few.
NLP uses a variety of techniques to understand human language, including machine learning, statistical modeling, and linguistic analysis. By analyzing patterns in large amounts of text data, NLP algorithms can learn to recognize and interpret language in a way that's similar to how humans do it.
Overall, NLP is a powerful tool for bridging the gap between humans and machines. It has a wide range of applications in industries like healthcare, finance, customer service, and more, and it's constantly evolving and improving as researchers and developers continue to improve the technology.
NLP helps RPA solutions understand written language just as humans do. Such software applications normally fall into two groups: those working with unstructured data and the ones working with structured or semi-structured ones. While the first group relates to invoices, insurance claims, medical files, financial filings, and so on, the second is about free-form content.
Overall, RPA with NLP capabilities can help to:
- Understand the context of the data source
- Connect to various enterprise applications that generate unstructured data
- Extract and validate relevant data while converting it into a structured format
Here’s an example of how NLP can be applied. Flyaps teamed up with a recruiting company to build CV Compiler, a tool that uses machine learning and NLP to analyze and enhance technical resumes, allowing job-seekers to get a job in companies like Google or Facebook. To make CV Compiler parse resumes with high precision and provide personalized recommendations in less than a second, our team used the NLP algorithm trained on more than 1M of tech resumes.
As a result, the solution we built is able to scan PDF files (which is the most popular format for creating CVs) and provide users recommendations on what they could improve in their resumes. Today, more than 50,000 IT professionals are using this solution to improve their CVs.
How to implement AI in RPA, and when do you need a custom solution?
To create an AI-driven RPA solution, many businesses use ready-made tools and low-code application platforms, and AI development platforms, which saves their developers time and resources. There are many tools like UiPath or BluePrism that could help you speed up the development process thanks to ready-made templates and drag-and-drop features. For example, UiPAth says it could help you build business apps with low-code visual tools, or it can also combine UI and API automation for maximum scale and speed across the broadest range of systems.
But the truth is that off-the-shelf software solutions and LCAPs can’t meet the unique needs of every business. For example, when we were building the CV Compiler, we first used DaXtra, a ready-made solution, which was responsible for parsing CVs, and searching for relevant vacancies. But because DaXtra targets big enterprises that are not necessarily ICT-related, it wasn’t a perfect solution for our app. We’ve run into several performance issues, and DaXtra API was not able to identify tech words accurately, slowing down the process of CV parsing and the quality of CV analysis overall. So we decided to build our own neural network focused solely on the ICT domain. This allowed us to significantly increase the speed of CV parsing while reducing the number of errors.
Our example shows that sometimes opting for custom development is a wise thing to do. Here are some situations where you may require it instead of using ready-made tools:
- Unique business requirements: If your business has unique requirements that cannot be met by off-the-shelf solutions, a custom solution is your go to. For example, if you need to automate a process that involves proprietary software.
- Legacy systems: When your business relies on legacy systems that are not compatible with off-the-shelf solutions, this is another case to opt for custom development. This could involve building custom connectors or using APIs to enable the legacy system to interact with the AI and RPA solutions.
- Complex processes: Lastly, choose custom development if you want to automate complex processes that involve both rule-based and intelligent decision-making.
Read also: Automation Examples and Success Stories
Conclusion
“The first rule of any technology used in a business is that automation applied to an efficient operation will magnify the efficiency. The second is that automation applied to an inefficient operation will magnify the inefficiency.”
Bill Gates.
AI and RPA do help to streamline business processes, letting your employees complete tasks efficiently and with a minor risk of mistakes. But in all fairness, not everyone needs this combo. For example, if your daily business routine is all about simple and straightforward tasks, and if you have only structured data to work with, then integrating an RPA solution may be enough. So before you decide to build a solution that combines RPA and AI, make sure it’s something your business really needs. And when you’re curious to learn more in this regard, feel free to read our article about business process automation, where we highlight key steps for implementing it.
We’re also glad to give you a consultation and help you create your own automation strategy. Just send us a note and we’ll come back to you shortly!
Skip the endless hiring cycles. Scale your team fast with AI/ML specialists who delivered for Indeed, Orange, and Rakuten.
Scale your team





