How to Automate Business Processes: A Step-by-Step Guide to Streamlining Your Business

When your company grows — it's a good thing. But the number of tasks and processes that you and your employees have to manage increases as well. As a result, your day workloads continue to pile up, along with mistakes, stress and burnout for you and your employees. And this is a bad thing.
But there is a solution – business process automation. By automating some processes, you can grow more efficiently. Over the past 10 years, Flyaps has been helping businesses from different industries streamline their workflows with custom-built automation tools. We've found that using RPA, AI development platforms, and low-code platforms to automate our clients' business processes frees up resources for more important things like strategic planning, innovation, and taking care of customers.
In this article, we are going to share eight steps to automate your business operations. We'll also provide examples from our own experience, highlighting the solutions we've built and the positive results they've delivered for our clients. Let's get started!
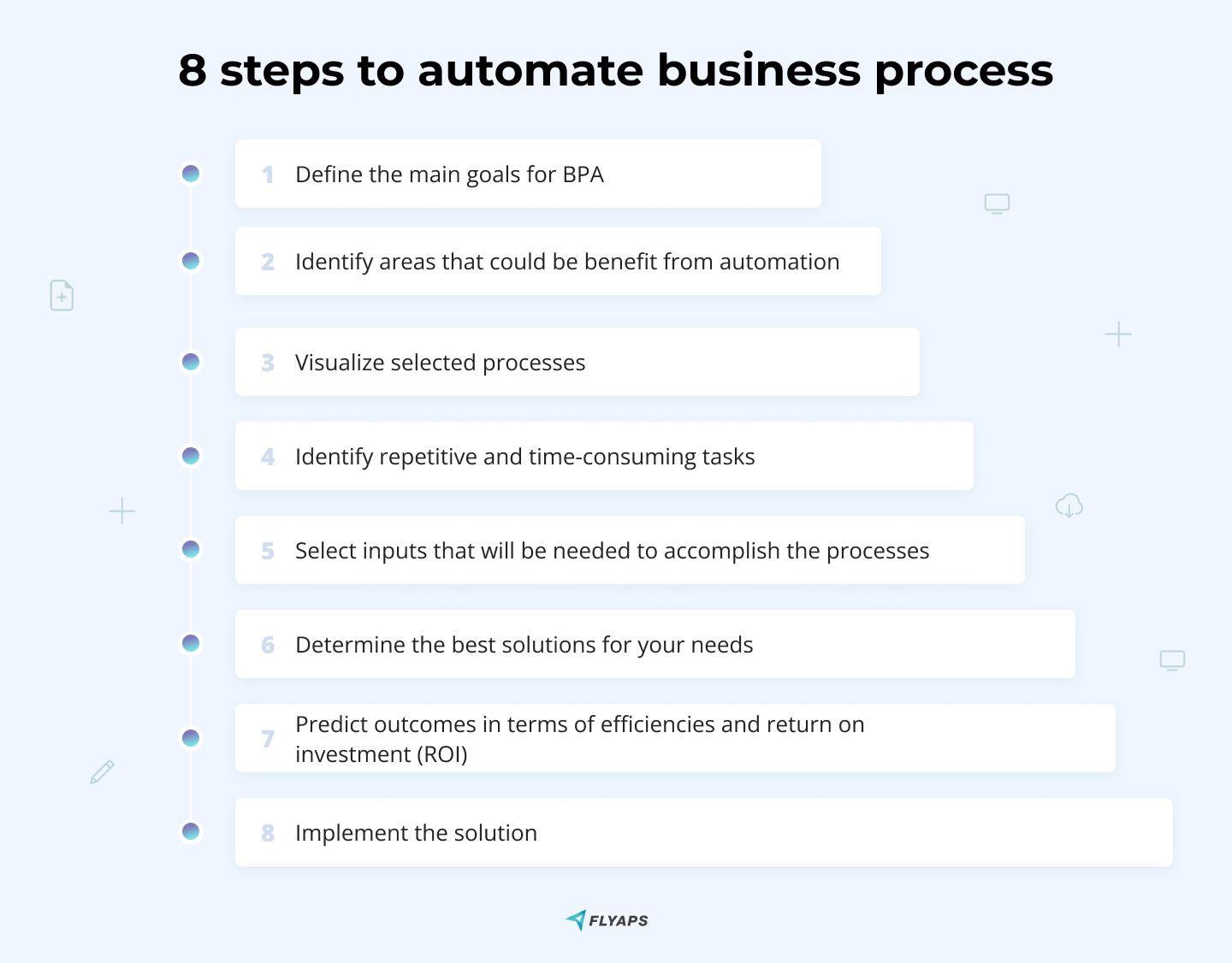
Step 1: Define the main goals for BPA
Automating your business processes without proper business process automation strategy is like planning a road trip without any destination. Sure, you can hop in the car and start driving. But, putting the thrill of adventure aside, you might end up wasting time and resources in vain.
Similarly, identifying your main objectives for business process automation is crucial to achieve specific goals. So, ask yourself: What are you expecting to get by implementing a business process automation strategy? Here are some possible answers:
- Reduce labor costs.
- Improve the quality of the output and reduce human error.
- Reduce the time and effort required to complete tasks.
- Enhance visibility by providing real-time data and analytics to monitor and optimize processes for better performance and results.
- Enhance compliance with regulations and policies.
Read also: What Is Business Process Automation?
Step 2: Identify areas that could benefit from automation
After defining the goals for your BPA project, it’s time to look for areas to automate. For example, you’ve decided to reduce labor costs. Are there any areas in your company that fully depend on manual labor? Like customer service, or accounting, for instance? Those will be your most obvious candidates for automation.
Here are a few examples of areas that could be improved by business process automation:
- Customer service to reduce labor costs: Imagine you have an online shop and your customer service representatives are always busy dealing with thousands of support tickets. It’s time for automation then. By implementing an AI-powered chatbot to address your clients’ questions, you will kill two birds with one stone: your customers could get an answer to their questions within seconds, while your employees will spend less time dealing with repetitive tasks.
- Recruitment to speed up hiring: Let’s say, your company is growing and there are a lot of new positions in the IT department your recruiters struggle to close. The best candidates are accepting offers from other companies before you even have a chance to invite them to a technical interview. Seems like your competitors have found a way to speed up their hiring. And indeed, after checking the market, you discover that there are tools to automatically screen job applications and filter out unqualified candidates. Again one point goes to automation.
- Marketing to increase sales: Imagine you work as a marketer in an online bookstore. One day, analyzing customer data, you noticed that customers who had previously bought novels in the "books that were made into movies" category were not returning to purchase books from other related categories (like “modern authors”). To encourage these customers to explore the bookstore's other offerings, you’ve decided to set up an automated email campaign that sends targeted messages with recommendations for books in those related categories. As a result, sales from returning customers increased by 25%.
Step 3: Visualize selected processes for BPA
At this stage, you know your goals and you understand what areas are the most promising in terms of business process automation. But how can you reveal where gaps, latency and bottlenecks exist? The answer is visualization.
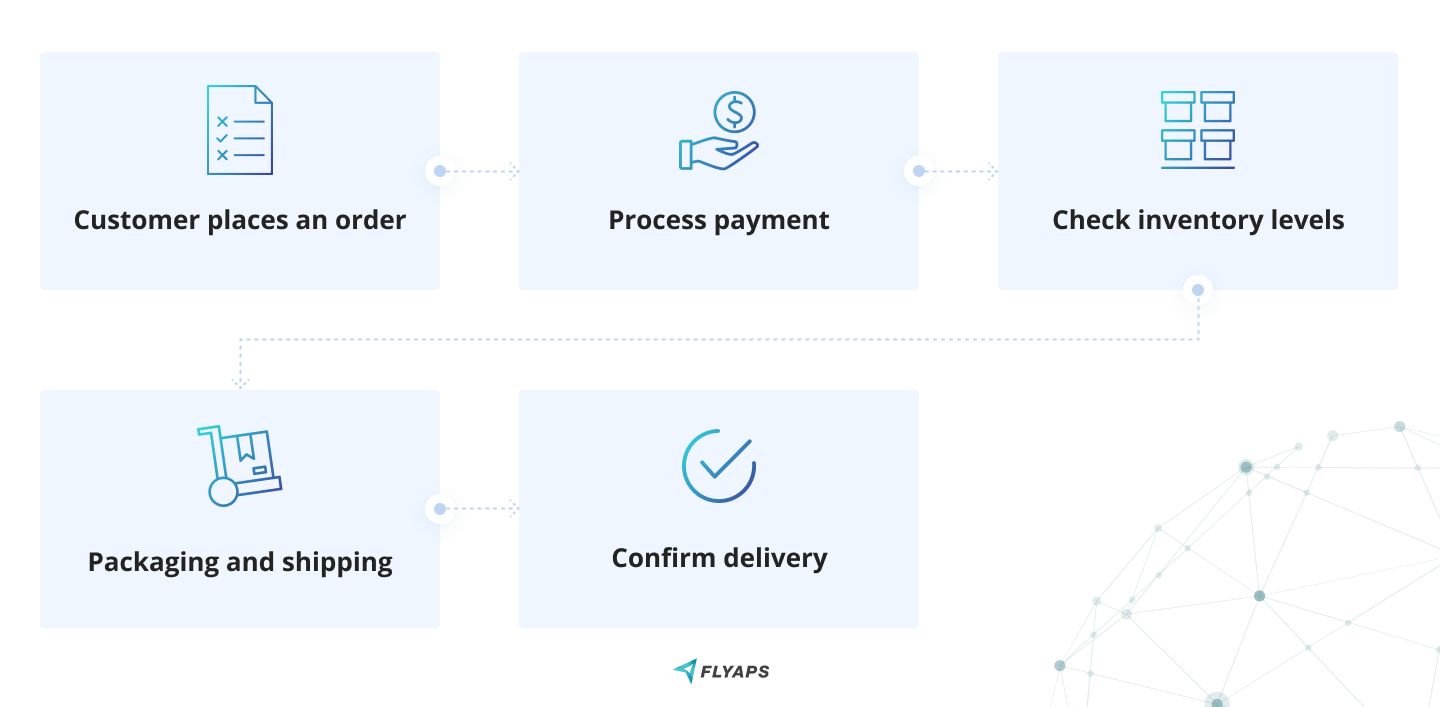
Let’s say, your goal is to reduce errors when it comes to online sales. To research where errors come from, you need to split the whole process into stages and write out actions taken at each stage. The easiest way is to use a flowchart to break down the process into specific links that form an online sales processing chain. Flowcharts are diagrams that show the sequence of steps in a process or system. By adding details such as time to complete a task and so on, flowcharts will allow you to identify where a process may be getting stuck or slowed down.
Here’s how a flowchart may look:
There are several other methods for visualizing business processes:
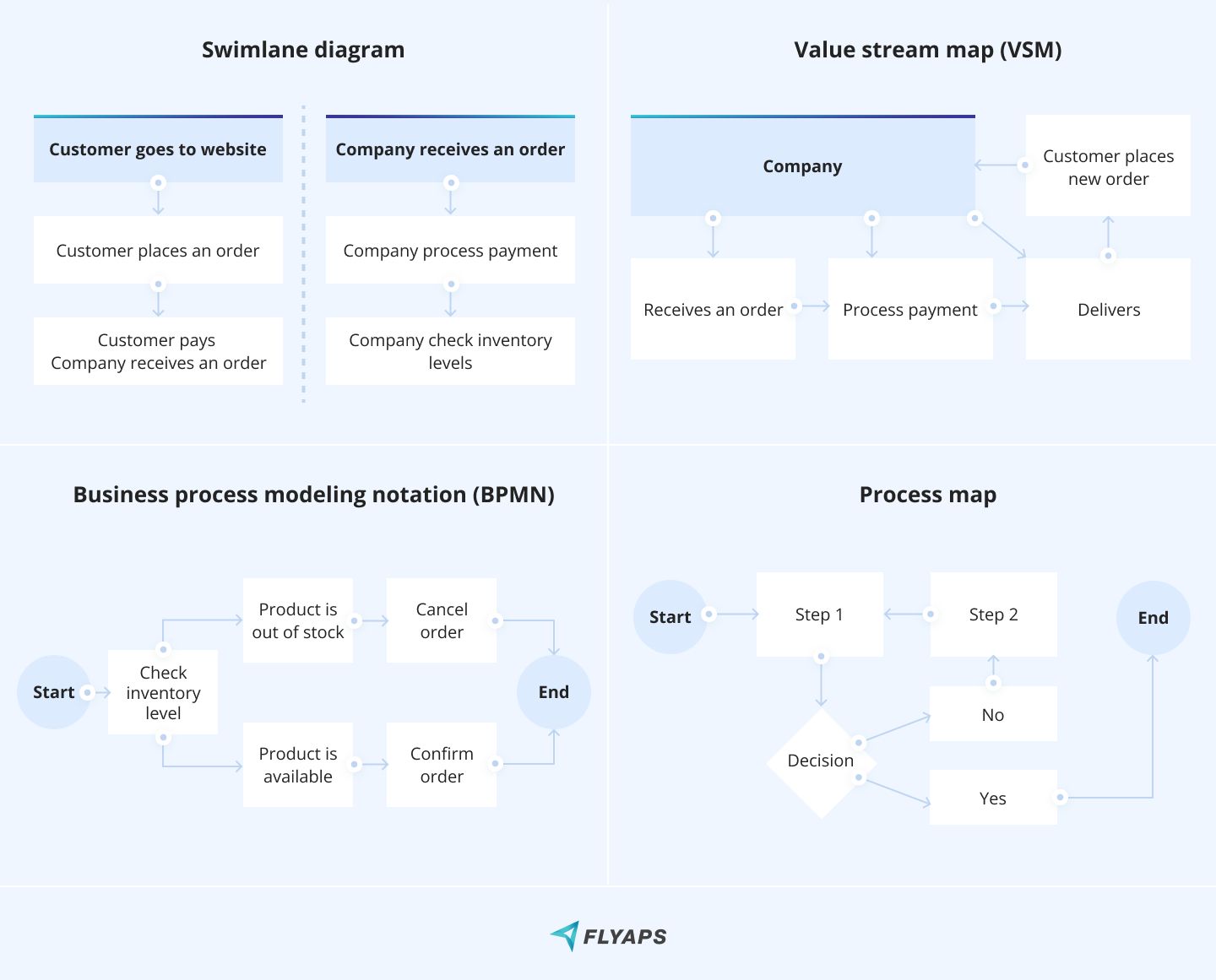
- Swimlane diagrams — are a type of flowcharts, which shows who's doing what in a process. Think of it like lanes in a pool. The diagram splits the process steps into horizontal or vertical "swimlanes" assigned to a specific worker, team or department. This way, it's clear who's responsible for each step and who to hold accountable.
- Value stream maps (VSM) — are diagrams that show how materials and information flow through a process. For example, a VSM for a car manufacturing process can show how parts are delivered from suppliers to the assembly line.
- Process maps — are similar to flowcharts but focus more on the details of each step. They're often used to document standard operating procedures. For example, a process map for a coffee shop might use symbols to show the steps involved in making a latte, including the amount of espresso shots, milk, and foam needed at each step.
- Business process modeling notation (BPMN) — it uses symbols and notation to define process flows, decision points, and other elements. For example, a BPMN diagram for a software development company might show how code is developed, tested, and released to customers.
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) — are detailed documents that describe how a process should be carried out. They're often used for complex or critical processes. Use a clear and concise writing style, and include step-by-step instructions, process diagrams, and quality control measures.
Step 4: Identify repetitive and time-consuming tasks
With a previously visualized process, it should be easy. Tasks that are repetitive and take up a lot of time and resources are perfect candidates for automation.
Suppose, you’ve discovered that checking inventory level is taking up to three days on average per order. Quite a lot of time for customers to change their minds, don’t you think? Also, let’s not forget about shipping delays and complaints your customer service will have to deal with as a result. Looks like the process of checking inventory should be automated.
Step 5: Select inputs that will be needed to accomplish the processes
Let's say a hospital wants to automate its patient check-in process. In order to do this, they need to identify what information is required from each patient, such as their name, date of birth, and reason for the visit. Without identifying this input, the automation system is not able to check the patient in, which could lead to delays and frustration for both the patient and the hospital staff.
The data can be structured and unstructured. It is important to identify these two types of data because you might need different technologies to process them.
Structured data refers to data that is organized and easy to search through. Consider it as a spreadsheet with columns for different types of information. For example, you might have a column for customer names, a column for customer addresses, a column for customer phone numbers, and so on.
On the other hand, unstructured data is not organized in a specific way and can be more difficult to search through. This includes text such as emails, social media posts, blog articles, and news articles. Images and photographs are a common form of unstructured data. They can be difficult to process and analyze without advanced image recognition technologies. Audio and video recordings, as well as surveillance footage, also refer to unstructured data.
Step 6: Determine the best solutions for your needs in business processes automation
Now, it is time to choose solutions that will suit your company needs best. You have three types of solutions to consider when it comes to business process automation: pre-built tools, low-code BPA platforms, and custom software.
Pre-built tools
Pre-built tools are ready-made software that is designed to automate specific business processes. These tools have a set of features that can be used straight out of the box or slightly adjusted to meet your specific needs. Compared to the other two solutions, the level of customization for pre-built tools is minimal. As a result, they are most appropriate for businesses that have relatively uncomplicated and standard processes that don't require extensive customization.
Pre-built tools are highly popular in the HR & recruitment industry. To simplify the process of candidate screening and reduce the overall time to hire, companies opt for automation tools that can analyze the candidates’ CVs in minutes and conclude whether they are the right fit for the position. CV scanner and Chrome Plugin built by Flyaps for GlossaryTech, is an on-point example of a pre-built tool that helps optimize the hiring process.
Candidates use different platforms and templates to create their resumes, so Flyaps’s focus was on finding the best way to process unstructured data. We used natural language processing (NLP) technology to enable the Chrome extension to read CVs and extract important information for recruiters. This way, recruiters can find relevant candidates in minutes. For example, the extension can differentiate between Java and JavaScript and recognize candidates with expertise in backend development, even if the word "backend" is not explicitly mentioned in the resume.
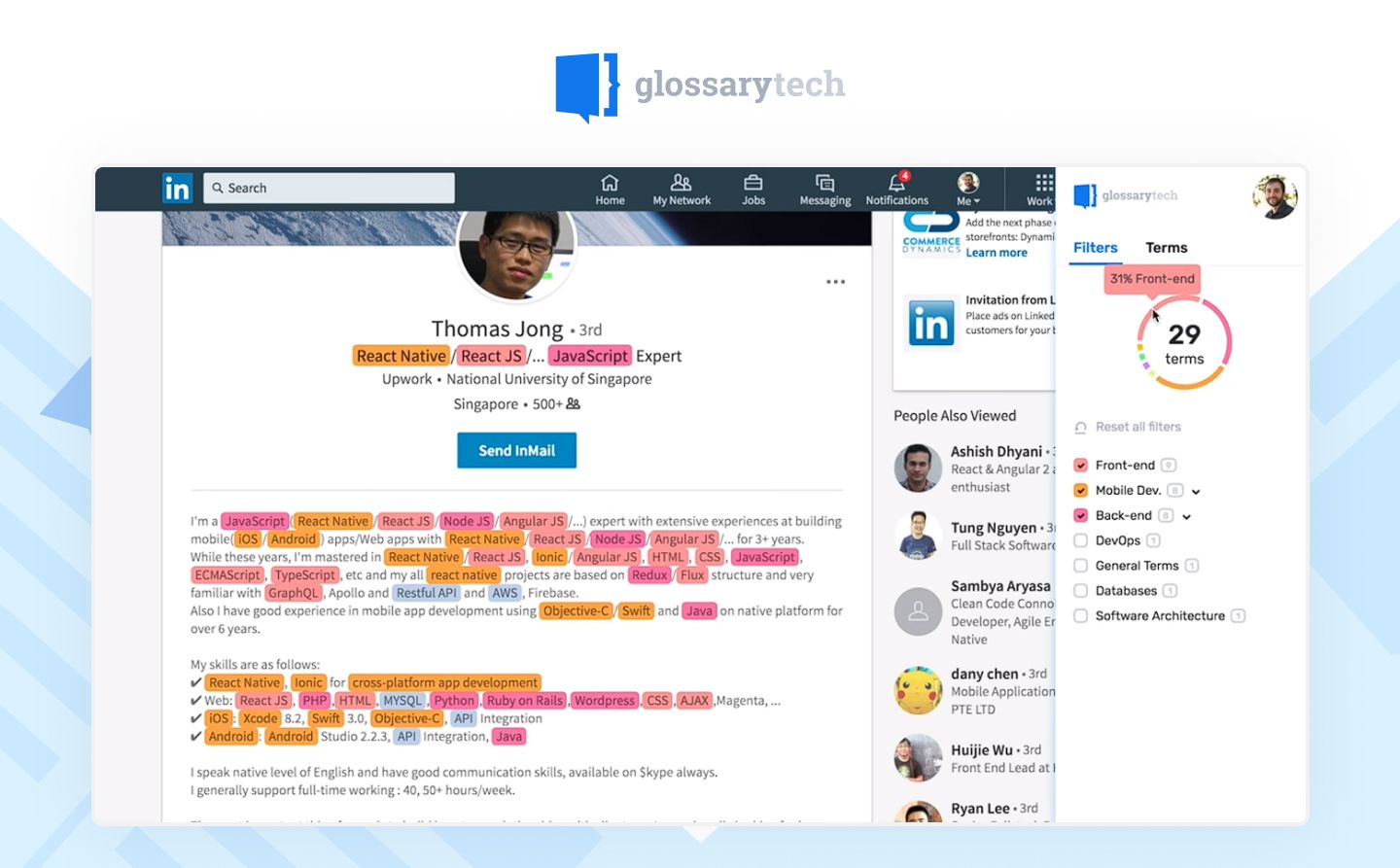
This enables recruiters to make faster and more informed decisions when reviewing job applications.
Low-code BPA platforms
Low-code business process automation platforms are software applications that enable developers to create customized automation solutions quickly and without the need to write extensive amounts of code. Low-code platforms provide a visual interface and a set of building blocks that tech specialists can use to create custom workflows and integrations. Such platforms are best suited for businesses that need a higher level of customization than pre-built tools can provide but don't have the time and resources needed to build a fully custom solution from scratch.
Airbyte is an excellent example of a low-code platform that Flyaps helped to develop. It is an easy-to-use solution for businesses that want to automate their data transfer operations.
For example, your marketing department wants to analyze customer data to build a more effective marketing strategy. You have multiple sources of customer data, such as social media platforms, CRM systems, and email marketing tools. To analyze this data effectively, your data engineers need to bring all the data into one place, such as a data warehouse. This can be a tedious and time-consuming task for tech specialists which requires a lot of coding.
With Airbyte, your data engineers can easily automate this process by setting up data connectors for each data source, specifying the transformation rules, and scheduling the data transfers. This way, an operation that normally takes several days or even weeks is reduced to mere 30 minutes.

Airbyte has become one of the top open-source data integration platforms with over 300 connectors. To build this platform, we used Python – a language preferred by data engineers (Airbyte's target audience). We also integrated quality control measures to ensure the community-built connectors match Airbyte's protocol and have correct configuration. The quality control process includes assigning a grade for reliability and verifying the connector before adding it to the Airbyte catalog.
Read also: Low-Code Business Process Automation : A Look at the Possibilities and Limitations
Custom software
In this case, a fully customized solution is created specifically for your business from scratch. This type of software is perfect for businesses with complicated processes that need a high level of personalization but is also the most complex one to implement.
Custom solutions are popular in the telecom industry, where each enterprise has unique requirements, and ready-made tools can’t satisfy them - but they also require a clear understanding of costs, especially when AI is involved (here’s how much AI costs to make in 2025). Let us give you a real-life example.
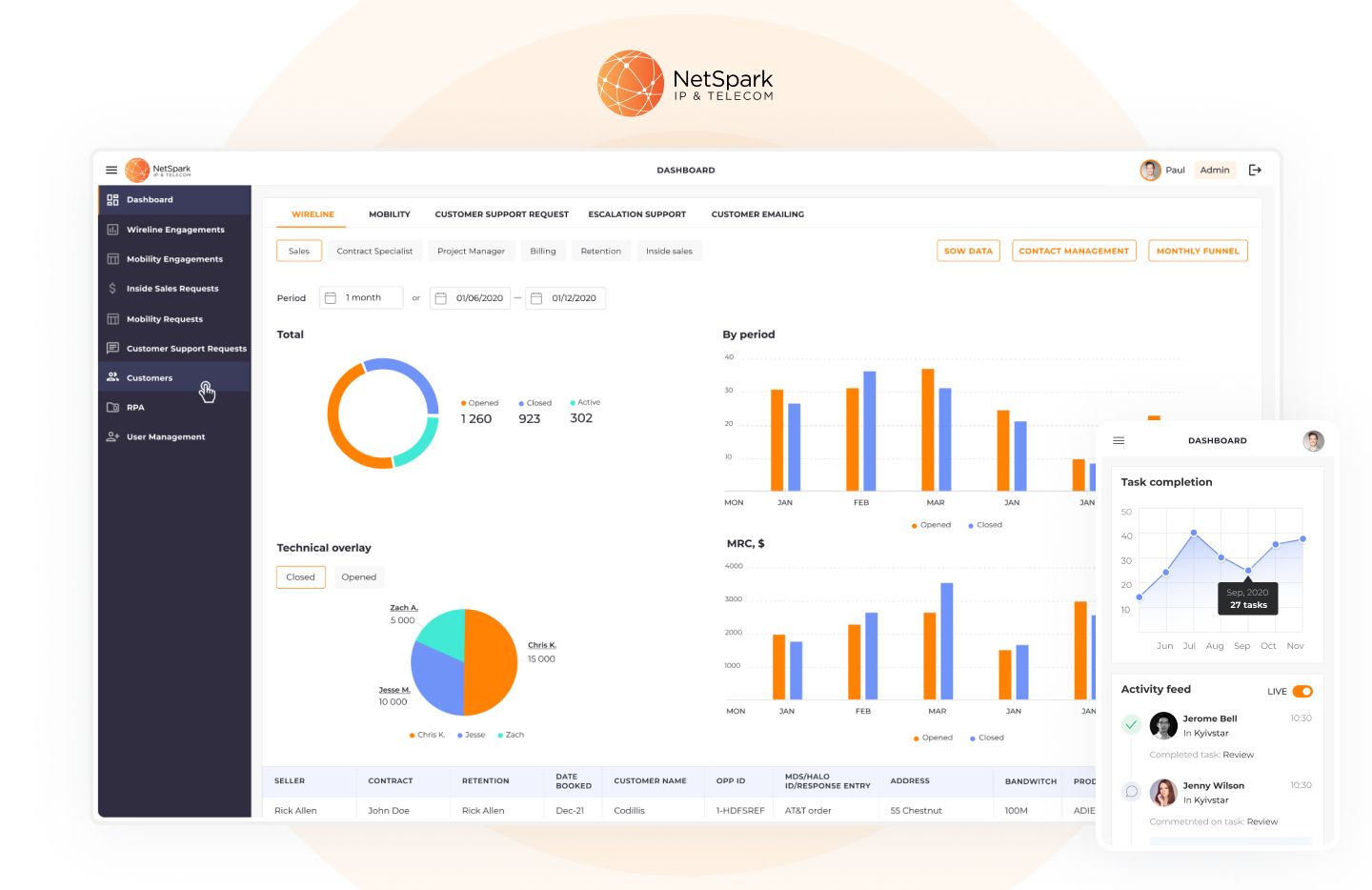
Before working with us, NetSpark IP & Telecom, a telecommunications consulting company, didn’t have any automation solutions. However, as their business grew, they struggled with the manual workload, particularly when it came to determining the optimal tariff plans for each client. This process required up to 10 employees to work on a single project simultaneously.
NetSpark, lacking in-house technical experts, turned to Flyaps for a solution to their manual workload. Flyaps developed a custom CRM/ERP system and a calculation tool using Python (Django), React, and Material UI, enabling NetSpark to automate the process of analyzing client data and suggesting optimal tariff plans. The solution offers various user roles and access rights, so it may be used by NetSpark employees as well as AT&T representatives and customers.
With the first version of the custom CRM/ERP system launched in just three months, NetSpark was able to reduce manual work, improve team performance, and increase revenue.
Step 7: Predict outcomes in terms of efficiencies and return on investment (ROI)
Now, it is time to count what effect you expect after implementing your business process automation strategy and how to measure its progress.
- Set clear goals: Determine how much time, money, and resources you expect to save, and how much additional revenue you expect to generate.
- Measure current metrics: Processes you are about to automate have clear metrics. Measure the current metrics, including the time it takes to complete the task, the cost of the process, and any errors or delays that occur.
- Estimate the costs: Estimate the costs associated with implementing the automation solution, including any necessary hardware or software, personnel, and training.
- Calculate the expected ROI: Estimate the expected ROI by calculating the difference between the cost of the automation solution against savings and revenue you will get over a set period of time.
Step 8: Implement the solution
Once you've figured out what solution you will use and predicted the outcomes, you can start implementing your business process automation strategy. This means integrating your solution with other business processes in your organization, making it user-friendly, and teaching your staff how to use it.
For example, say your company is implementing a new CRM software to streamline customer management processes. To fully integrate this software into your existing business processes, you need to connect it with sales and marketing tools, as well as billing and payment systems. Additionally, your staff members who will be using the software need to be trained on how to input customer data, generate reports, and track progress, ensuring the software is used effectively.
Conclusion
If you're considering implementing a business process automation workflow, you've got a lot of decisions ahead of you. It's not always an easy task, and without the right knowledge and expertise, it might take a lot of time. But don't worry, we're here to help.
At Flyaps, we specialize in custom software development, and we've got a ton of experience creating automation tools for different domains. We can guide you through the process and save you a lot of time and hassle. So if you're ready to revolutionize your business operations, just drop us a message and let's get started!





