Smart Contracts for Businesses

The blockchain and the opportunities it offers are transforming how we conduct business and even our day-to-day lives. A small computer program stored on a blockchain called a smart contract can reduce time and expenses and optimize transactions. In this article, we will discuss the features of trust-shifting technology known as smart contracts, which industries could benefit from them, and some use cases.
What are Smart Contracts?
The concept of smart contracts was introduced in the 1990s by American computer scientist Nicholas Szabo. Their purpose was to design «highly evolved» E-commerce protocols on the Internet arranged between strangers.
The idea behind a smart contract is that it is a small computer program that is housed on a blockchain. There are a lot of blockchains that support smart contracts, the biggest one being Ethereum. This platform was designed to work with smart contracts, which can be programmed in a unique programming language created specifically for Ethereum called Solidity. It uses syntax that resembles Javascript. For those interested in exploring the broader scope of advanced software creation, including AI solutions, check out our article on AI development platforms and learn how much it costs to build an AI solution in 2025.
Smart contracts, in a nutshell, are similar to vending machines in that they accept payment for products based on displayed prices without the need for a middleman. A user pays a gas fee when using smart contracts (a gas fee is a cost needed for individuals to complete a transaction on a blockchain). A contract then executes transactions via computer code.
Another notable feature of smart contracts is that they run on Blockchain. Let's take a look at how a Blockchain-based smart contract looks. As an example, we will consider the ride-sharing service Lyft. This application's transactions are stored in the company's data centers, which can be expensive.
If one tried to replicate Lyft on a smart contract platform like Ethereum, the data would be held on a decentralized ledger owned by individuals running the network, eliminating the need for such high costs.
As a result, the gas fee you pay Ethereum is theoretically much lower than the fee drivers pay Lyft.
Smart Contracts Use Cases
Smart contract applications are frequently used for financial purposes such as trading, investing, making loans, and incurring debt. They can be used to set up entire corporate structures, as well as for gaming, healthcare, and real estate industries. These industries are built around a set of rules, algorithms, and measurable terms of engagement.
Banking institutions can use smart contracts to issue debt or make automatic transactions. The insurance industry can use this technology to optimize specific requirements, such as if a person has an insurance contract that states that if a certain event occurs, he will be paid a certain amount. The client is not required to do anything or contact the insurance company; the funds are automatically credited to their account.
Due to their self-executing nature, these contracts are preferable to certain industries than others. Automated contracts are less appropriate for industries requiring high service levels, such as hotels, hospitals, or restaurants.
Smart contracts may also benefit the following industries:
- Startups
- Venture Capital
- Supply Chain
- Charities
- Education
- Transport & Logistics
- Warehouse
- Agriculture
- Travel & Tourism
Benefits of Smart Contracts for Business
Despite the impressive popularity, people are still wondering why they should switch to smart contracts when traditional legal agreements have worked well all these years.
Smart contracts already have many advantages over traditional agreements. As technology advances, this figure is likely to rise. Here are some of the most significant advantages of using smart contracts.
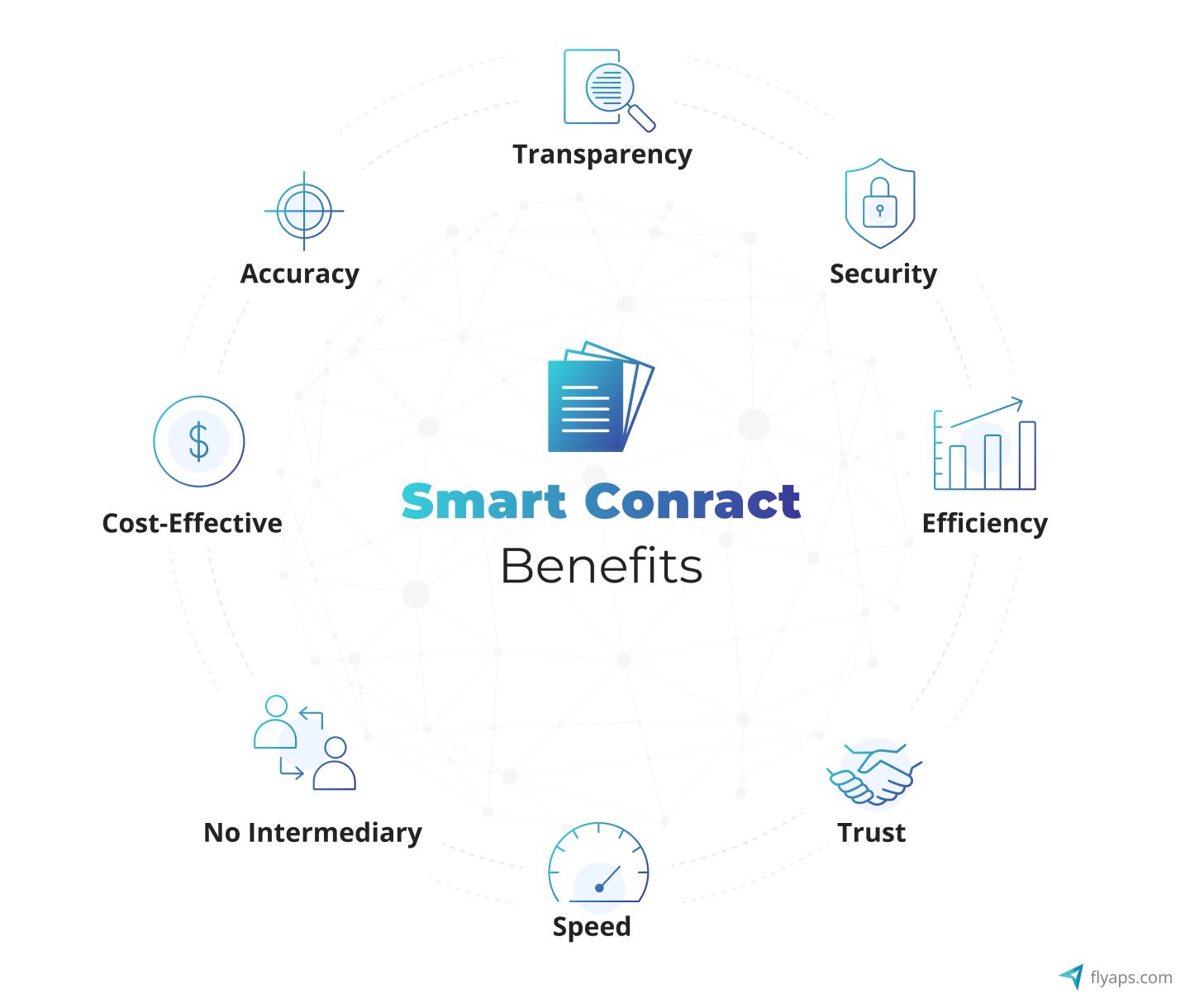
No third parties
One of the most significant features of smart contracts is that they do not require a third party to run. This technology not only reduces middleman risk but also saves a lot of resources for the company. In real estate, for example, the fee for intermediaries such as lawyers, brokers, and other individuals involved in the transaction can be prohibitively expensive. Blockchain eliminates the need for such third parties.
Transparency
Thanks to blockchain technology, once created, smart contracts can never be changed again. The code cannot be changed behind your back. Everyone on the network validates the output of the contract. Fraud is, therefore, unattainable because others will spot the attempt and mark it as invalid.
Smart contracts' terms and conditions are fully visible and accessible to all relevant parties. Once the contract is established, there is no way to dispute it. This ensures that the transaction is completely transparent to all parties involved.
Minimizing costs
This advantage is also linked to the elimination of intermediaries. The associated costs are reduced because there is no need to rely on a third party to verify the terms of the contract and provide the necessary confidence. Intermediary fees are eliminated in this type of contract.
Speed
For many industries, the elimination of the need to manually process documents sounds appealing in terms of time savings. In traditional scenarios, transaction completion can take weeks, months, or even years. This inconvenience is eliminated by implementing a simple, smart contract. Thoughtful computerization replaces paperwork.
Smart contracts are based on code and are accessible via the Internet. As a result, they can complete transactions in record time. This factor has the potential to accelerate many traditional business processes, bringing buyers and sellers together more directly and quickly than ever before.
Security and Trust
Data encryption at its highest level is used by automated contracts, which is also the standard used by modern cryptocurrencies. This level of security places them among the most secure items on the internet.
Smart contracts generate complete confidence in their execution. The agreement's transparency, autonomy, and security rule out any possibility of manipulation, bias, or error. Following its official announcement, the network automatically fulfills the contract.
The parties agree to follow the rules and definitions of the base code by using a self-executing contract. This significantly reduces, if not completely eliminates the need for court proceedings.
Smart contracts VS Traditional contracts
In 1997, when Nick Szabo introduced smart contracts, his sole purpose was to use a distributed ledger to store contracts. Nowadays smart contracts are just like the traditional version, with a single difference being purely digital. Smart contracts are essentially computer programs that automate the enforcement of conditions. Traditional contracts, on the other hand, are collections of mutually agreed-upon terms that are legally binding and described in natural human language.
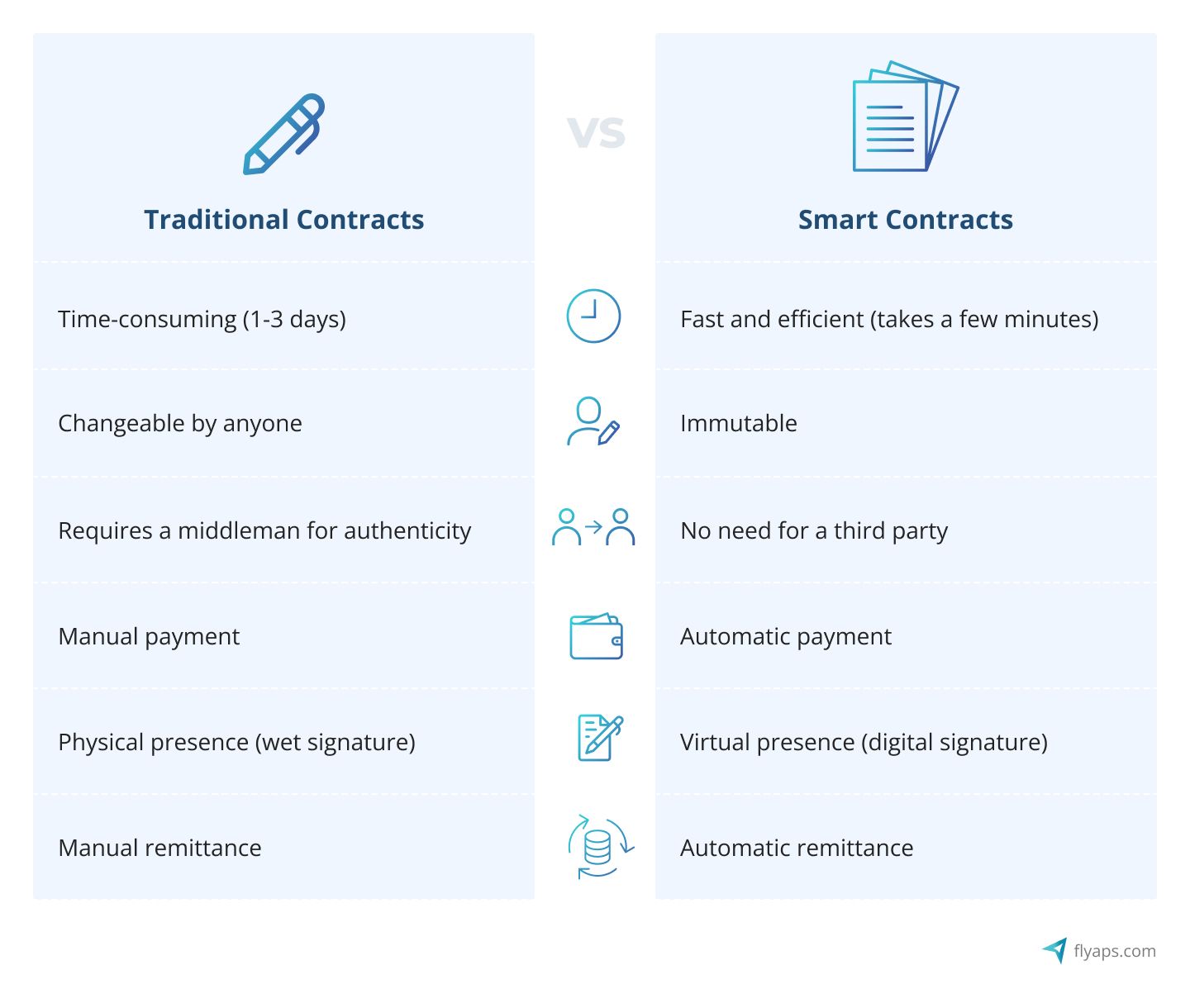
It can be argued whether smart contracts can replace traditional contracts as they both serve different purposes. Traditional contracts are executed in a complex and unsettled real world, in which smart contracts are sometimes extremely difficult to incorporate. A smart contract works well when the terms are clear, objective, and quantifiable.
Conclusion
Smart contracts are a digital alternative to paper contracts that offer significant advantages in terms of lower transaction costs, increased process efficiency, and data security. Depending on the industry, smart contracts may be more beneficial in some cases than in others.
However, smart contracts' widespread adoption will be a gradual process. If you decide to automate smart contracts for your company, make sure you do your homework. Consult with legal and technical experts to ensure that the final code meets your requirements and is safe from malicious external attacks.