Navigating Generative AI Compliance: 4 Risk Management Strategies

Generative AI technology and the rules that govern it are constantly being updated. Therefore, CEOs and CIOs often worry about generative AI compliance when considering gen AI adoption. As regulations can be a big hurdle to the adoption, many choose a cautious approach, even pausing to closely monitor the situation. This careful decision is wise because quickly embracing generative AI without proper planning can lead to negative outcomes.
Some big players in this tech, like OpenAI and Google, are feeling the heat with regulatory inspections and legal problems. For instance, Google is in a lawsuit accused of using copyrighted content and personal info of millions of Americans improperly to train its AI products, including the chatbot, Bard.
As an AI-focused software development company with more than a decade in the field, we at Flyaps have encountered various compliance issues, AI-related too. In this article, we will share four proven strategies for successful generative AI compliance. But let’s start with the most common reasons why without proper strategy your gen AI project might fail.
What causes legal challenges with generative AI compliance
Generative AI is a great technology for helping companies from different industries identify potential compliance issues. However, when it comes to generative AI itself, a new set of considerations emerges.
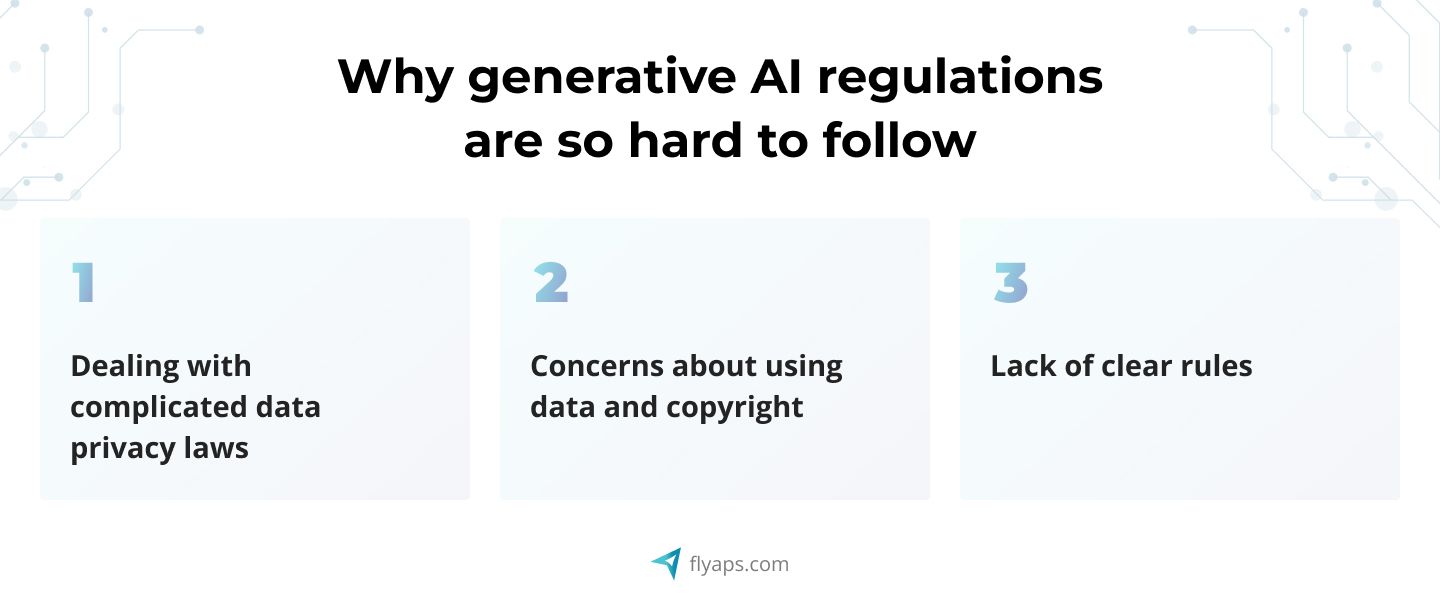
1. Dealing with complicated data privacy laws
It is especially difficult to cope with if a company operates globally. Even different states in the U.S. have their own data privacy law regulations! Companies might find it hard to follow and understand various complex data privacy laws, but not following them could result in legal issues.
2. Concerns about using data and copyright
There's a chance of using copyrighted data by mistake during AI training. This could cause legal problems and disputes over intellectual property unless companies get the right permissions or licenses for using such data.
3. Lack of clear rules
The world of generative AI is always changing, and there are no well-established rules or regulations to handle its unique challenges. This lack of universal rules creates the need for companies to keep up with changes in the law and adjust their plans accordingly.
While it all sounds quite gloomy, there are strategies that companies successfully employ to implement and harness the benefits of generative AI.
Top strategies for successful generative AI compliance
As mentioned, generative AI is a dynamic field, and staying on the right side of the rules means always monitoring changes that appear. But while it’s a very complicated process, you can adopt certain strategic approaches that make it easier to comply with changing standards.

Cautious deployment
To minimize potential risks, some companies are playing it safe with generative AI. They choose to limit its use and only deploy it in areas where the risks tend to be the lowest.
For example, in energy companies, AI is used to help employees leverage geologic surveys and reports, making complex information more accessible. Most companies are starting by augmenting internal users, providing them with smart research assistants for tasks like summarization and generating text drafts. This cautious approach allows them to benefit from AI without exposing themselves to high risks.
Gen AI is great for marketing tasks as it helps come up with new ideas and content that works well for social media and blogs. However, it's not a good idea to use public chatbots, like ChatGPT, for reviewing medical records and bills, particularly without obtaining clients' permission. In this case, we’re talking about sensitive data, and there's a risk that the platform might collect and store it.
Open-source approach
Some companies are concerned that commercial gen AI models are not transparent enough. Therefore, to reduce data privacy risks, they choose open-source AI models that are more customizable and provide fine-tuning options. It allows their systems to operate on-premise or in private clouds. Meta's Llama 2 is a great example of an open-source gen AI model. It is a large language model (LLM) that is available for free for applications with less than 700 million monthly users.
However, while open-source software offers flexibility, it still comes with some cybersecurity risks. Synopsys report confirms that 84% of open source codebases have vulnerabilities. To address this issue, organizations are running these open-source AI models in secure environments, reducing the risk of data loss and ensuring compliance with data sovereignty rules.
But despite the benefits, open-source software presents security risks that require organizations to establish controls for AI models similar to other software projects. Involving information security and compliance teams is critical when dealing with open-source solutions.
Choosing indemnification-backed collaborations
Imagine a scenario where a marketing company, let it be ABC Marketing, decides to use an advanced image-generating AI to create visually appealing content for their clients. They are considering a cutting-edge AI model from a vendor, but they are concerned about potential legal issues related to copyright violations in the training data.
Aware of these concerns, ABC Marketing chooses to work with established vendors known for their reliability and commitment to legal compliance. They opt for Adobe's image-generating AI, which, along with platforms like Shutterstock, ensures that the AI is trained only on fully licensed or public domain data, minimizing the risk of copyright infringements.
The marketing company is imaginary, but Adobe and Shutterstock do provide indemnification. Adobe even went a step further by announcing that it would indemnify enterprises for content generated by AI, assuring them they can confidently use it throughout their organization.
Prioritizing data privacy on a top level
Prioritizing data privacy in generative AI goes beyond individual roles. It's a company-wide responsibility that starts at the top. With a significant increase in regulations governing data privacy, non-compliance can result in severe penalties and damage to a company's and its leaders' reputation. Therefore, top-level executives recognize the need to ensure that AI systems comply with these regulations to avoid legal consequences.
Similar to the evolution of cybersecurity and privacy, where boards now consider these aspects, AI is following the same trajectory. Just think of it, 15 years ago, boards weren't accustomed to thinking about privacy or having chief privacy officers. However, the landscape has changed, and privacy considerations are now embedded in the design of products and services. The same shift is expected with AI.
Closing thoughts
Successfully implementing generative AI through any of the mentioned strategies hinges on having reliable technical partners. Tech partners play a crucial role in navigating the complexities of AI implementation, ensuring that the chosen strategy aligns seamlessly with the organization's goals and industry regulations.
At Flyaps, our dedicated team of experts is committed to guiding you through every step of the gen AI implementation process. Whether you're prioritizing data privacy, exploring open-source models, or considering on-premises solutions, Flyaps is here to be your trusted technical ally.
Still feeling uncertain about navigating gen AI compliance within your organization? Drop us a line. We're here to provide the guidance and answers you need!

