GPT, Gemini… or What? How to Choose the Best LLM for Your Business

I won’t probably surprise you if I say that top large language models (LLMs), like GPT and Gemini, aren’t always the best solution for every project. While these popular LLMs have gained significant traction, simpler alternatives, such as rule-based systems or domain-specific algorithms, might do the job just as well.
So, why do many businesses still try some of the most popular, but not necessarily the best LLM models for their specific projects before exploring alternatives?
As an AI-focused software development team, Flyaps picks the best solution for each of our clients. Sometimes that means a top LLM, other times a lightweight, tailored solution designed for specific needs. If you need more details on that, check out our AI development services.
But let’s look at the most popular LLM models from all angles, the good, the bad, and the practical.
TL;DR
| → Popular LLMs excel in different tasks, like coding, reasoning, content creation, and enterprise search. |
| → API-accessible models are easier to deploy, while open-source options offer customization but require technical expertise. |
| → There isn’t a single best LLM for all business cases. Your choice depends on goals, budget, integration, scalability, and data privacy needs. |
Top LLMs can chat. But that’s not all
LLMs are the type of generative AI models that focus specifically on analyzing and generating text-based data. They can write articles, answer questions, translate, summarize, chat, and more. Here are some of the most popular functions LLMs are used for.
Translation
Models like GPT-5 often outperform Google Translate, especially for European languages, as they are more accurate in understanding idioms and context.
Content creation
Large language models dramatically changed marketing by automating the generation of various content types, from blogs to social media posts.
Alternative search tool
LLMs don’t just retrieve links or documents. They pull ideas together and give you context-rich answers that search engines usually miss. And Google came even further. They combined the Gemini model family with their traditional search index and rolled out AI Overview, a real-time summary of the web, right inside Google Search.
OpenAI, in turn, has recently launched Deep Research. It’s an agent that crawls through the internet, pulls from a wide mix of materials (text, images, PDFs), and then stitches it all together into something that reads like a polished analyst report.
AI agents and copilots
LLMs provide the core natural language understanding and generation capabilities that power copilots and AI agents. Instead of just answering questions, these systems can act. An AI agent can also carry out tasks, like processing a refund, updating account details, or scheduling an appointment. ChatGPT agent, for example, can summarize your schedule for the day or send invites on your behalf.
Copilots, on the other hand, sit side by side with human employees. They surface the right knowledge in real time, suggest next steps, and handle repetitive parts of a workflow so the human can focus on the judgment calls.
Code generation
Models like Mixtral 8x7B Instruct or Amazon Q Developer can generate code in various programming languages, significantly cutting development time. Developers describe what they want in plain language, and the model produces functional code snippets, templates, or even full applications.
LLMs have tons of uses, just like other generative AI. For a closer look at how they differ, see our LLMs vs. GenAI article .
Popular large language models might not always be the perfect fit for every use case, but the following tools are popular for a reason. Let’s see what makes the top LLMs shine.
The most popular LLMs: Are they really the best?
Everyone knows ChatGPT, and a lot have heard of Gemini. Claude is a bit less familiar, and Cohere? Even fewer know it. We’ll walk you through the most popular language models, along with those not widely recognized, so you can see what they’re good at and where they fall short.
GPT: One of the best LLMs existing
GPT is a series of models created by OpenAI. The flagship model is currently GPT-5, released in August 2025. It’s great for coding, reasoning, and agentic tasks across various domains. OpenAI says it’s their fastest and smartest model yet.
There are also GPT-5 mini and GPT-5 nano, which are faster and cheaper options. Mini is good for well-defined tasks, and nano is the most affordable.
OpenAI also offers other tools, including open-weight models (gpt-oss-120b, gpt-oss-20b), specialized models, like o3-deep-research or DALL·E 3, Sora, Codex, and more.
GPTs work great where there’s lots of text, repetitive workflows, or customer interaction. Businesses adopt them fastest in support, content, and internal knowledge automation. To get the full picture, let’s look at the pros and cons of GPT models.
Your business needs GPT because it:
→ Analyzes data and generates insights quickly.
→ Automates repetitive tasks like customer support, report writing, and email outreach.
→ Handles large volumes of interactions or content without extra headcount.
→ Can be tailored to company needs, tone, and processes.
But it would be wise to keep in mind that GPT models:
❗May miss key domain knowledge without fine-tuning.
❗Might be expensive in case of heavy use.
| GPT pros & cons | |||
| ✔️ Speed | ✔️ Efficiency | ✔️ Scalability | ✔️ Customization |
| ❌ Industry-specific gaps | ❌ Costs | ||
Book a consultation with our CTO to find the best LLM for your needs.
Learn moreGemini: The best AI LLM for handling visuals
Gemini is a group of LLMs created by Google AI and one of the best AI tools out there. Today, the latest model series is Gemini 2.5. Besides generating text like other LLMs, Gemini models can also understand and analyze images, audio, and video, without needing extra tools or modifications.
Gemini 2.5 series includes Gemini 2.5 Pro, 2.5 Flash, and 2.5 Flash-Lite. Pro is designed for complex tasks that require advanced reasoning. Gemini 2.5 Flash is optimized for high-speed performance with a balanced cost, while 2.5 Flash-Lite is the most cost-efficient and fastest model in the 2.5 line. The model is used in enterprise apps, customer support, creative industries, and education.
Let’s examine its strengths and weaknesses.
Your business needs Gemini because it:
→ Handles text, images, audio, and video inputs.
→ Works seamlessly with Android, Chrome, Google Photos, and Workspace.
→ Offers multiple models to balance speed, cost, and complexity.
→ Can provide more current info than other or its previous models because of its connection with Google search or fresh data sources.
But it would be wise to keep in mind that Gemini models:
❗May be expensive for small businesses.
❗Require developer knowledge and proper setup for tools and APIs.
| Gemini pros & cons | |||
| ✔️ Multimodal capabilities | ✔️ Integration with Google Services | ✔️ Flexibility | ✔️ Up-to-date information |
| ❌ Learning curve | ❌ Costs | ||
Claude 4: Built for better coding
Anthropic Claude 4 includes the Claude Opus 4 and Claude Sonnet 4 models. These are popular LLM models designed for advanced reasoning, coding, and AI agent workflows. Both models support extended thinking with tool use, memory improvements, and enhanced performance in coding, problem-solving, and complex multi-step tasks.
Opus 4 focuses on coding tasks and problem-solving, while Sonnet 4 offers a balanced, efficient solution for a wide range of use cases. Companies use Claude for customer support, knowledge management, multilingual communication, and training applications.
Your business needs Claude because it:
→ Excels at coding, software development, and automating complex workflows.
→ Supports multilingual communication and global operations.
→ Powers AI agents, customer support, and content generation.
→ Integrates seamlessly into IDEs and business tools.
But it would be wise to keep in mind that Claude models:
❗Could be costly for smaller teams.
❗ May show variable performance depending on the task.
| Claude pros & cons | |||
| ✔️ High-quality coding | ✔️ Multilingual capabilities | ✔️ AI agent power | ✔️ Integration |
| ❌ Cost | ❌ Variable performance | ||
DeepSeek R1: Works well for reasoning
When people talk about DeepSeek R1, two things come up right away: it’s open-source, and it’s strong at reasoning and data analysis. Released in early 2025 in China, this relatively young LLM is good at tasks requiring logical inference, solving mathematical problems, and assisting with real-time decision-making. On some key benchmarks, it may even edge out OpenAI’s o1.

With scores like these, DeepSeek R1 has firmly placed itself among the top-performing reasoning models in the world.
Unlike traditional LLMs that hand you an answer as if by magic, DeepSeek R1 shows its thought process. You don’t just get the “what”, you get the “how.” It makes a big difference when you’re dealing with complex problems where blind trust isn’t enough.
The model’s architecture is based on the Mixture of Experts (MoE) design, with 37B active parameters out of 671B total, and a 128K context window. Its 32B lightweight version achieves GPT-4-level math performance at 90% lower cost. Like most open models, DeepSeek R1 is available under an MIT license, and also as an OpenAI-compatible endpoint.
Your business needs DeepSeek R1 because it:
→ Demonstrates strong reasoning capabilities like self-verification, reflection, and generating long chains of thoughts.
→ Shows high performance across various benchmark evaluations, including mathematics, programming, and general logic.
→ Reduces costs, offering a more affordable alternative to competitor AI tools for both development and deployment.
→ Offers six lightweight distilled versions that lower computational requirements without sacrificing capability.
But it would be wise to keep in mind that DeepSeek R1:
❗ Performs best in English and Chinese, its accuracy in other languages can be limited.
❗ Tends to avoid or provide evasive answers on politically sensitive topics related to China, such as historical events or political issues.
| DeepSeek R1 pros & cons | |||
| ✔️ Enhanced reasoning | ✔️ High performance | ✔️ Affordability | ✔️ Flexible model options |
| ❌ Language limitations | ❌ Censorship sensitivity | ||
LLaMA: An open-weight AI for multimodal tasks
Large language model Meta AI (LLaMA) is an open-weight solution that everyone can find on GitHub. It comes in various sizes, including smaller ones requiring less computing power than GPT.
The most recent family of models is LLaMA 4, released in April 2025. This series includes natively multimodal models, LLaMA 4 Scout and LLaMA 4 Maverick, meaning they can understand and process both text and images.
The most obvious tasks for LLaMA would be writing articles, social media posts, novels, or video scripts. It is especially good for summarizing without missing important information. Here’s what else you should know about LLaMA.
Your business needs LLaMA because:
→ It is an open-weight model with a permissive commercial license.
→ You can fine-tune LLaMA on your own proprietary training data.
→ It shows impressive performance on a wide range of benchmarks, including coding, reasoning, and image understanding.
→ You can run LLaMA on-premises and keep sensitive business data safe.
But it would be wise to keep in mind that LLaMA models:
❗ Require significant technical expertise and hardware.
❗ Don’t offer the simplicity and robust support of proprietary APIs.
| LLaMA pros & cons | |||
| ✔️ Open-weight model | ✔️ Customization | ✔️ High performance on many benchmarks | ✔️ Data protection |
| ❌ High technical requirements | ❌ No turnkey support | ||
Falcon: A great combo of high performance and open accessibility
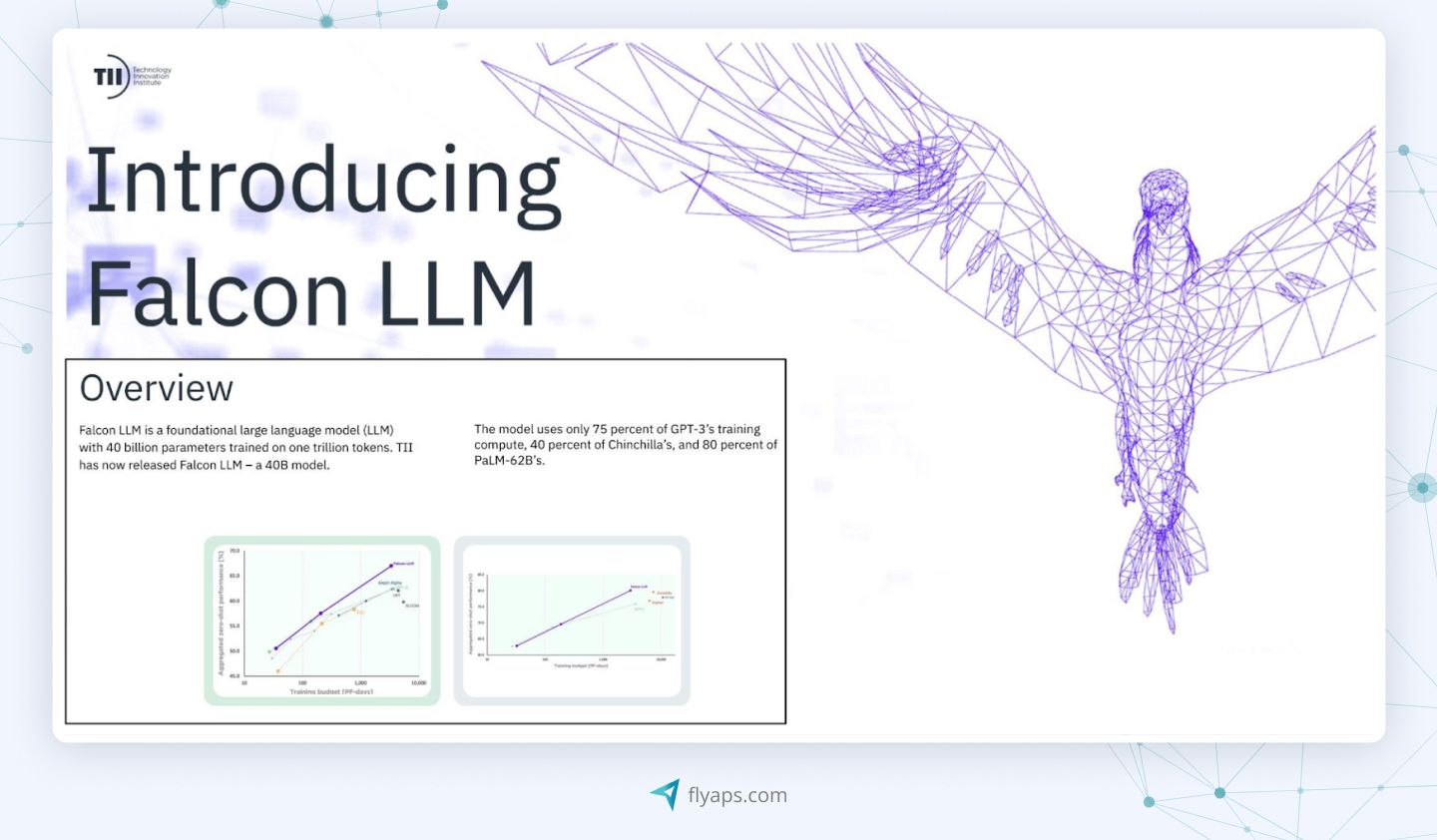
Falcon is one of the most powerful open-source language models that definitely outranks LLaMA while being based on it. It has a maximum of 40 billion parameters, but smaller versions with one to seven billion parameters are also available.
Falcon offers two model types: "base" for natural language processing tasks, and "instruct" for broader tasks. The base Falcon-40B requires significant GPU memory (90 GB), but still less than many LLaMA models. In contrast, Falcon-7B needs just 15 GB and can run on consumer hardware.
Falcon excels at specific tasks like generating articles and social media posts and creative content such as poems, scripts, and music. For chatbots, Falcon-40B enables natural, conversational interactions, making it perfect for customer support.
The model is also valuable for data augmentation, creating synthetic data resembling real-world examples. For instance, it can generate synthetic electronic health records for applications like disease diagnosis or treatment outcome prediction.
Your business needs Falcon because it:
→ Can be used, modified, and fine-tuned without the restrictions of a closed-source platform.
→ Demonstrates strong performance on various tasks, including reasoning, language understanding, and code generation.
→ Offers a range of models that cater to diverse applications from lightweight inference tasks to complex reasoning and generation.
→ Provides multimodal capabilities in later versions.
But it would be wise to keep in mind that Falcon models:
❗May not offer the same level of immediate enterprise-level support that is available from commercial, closed-source solutions.
❗ Require significant technical expertise to fine-tune.
| Falcon pros & cons | |||
| ✔️ Open-source model | ✔️ Customization | ✔️ Models for various needs | ✔️ Multimodal capabilities |
| ❌ Lack of immediate support | ❌ Need for AI/ML expertise | ||
Cohere: LLM models for enterprise apps
Cohere is an artificial intelligence startup that, apart from being an AI development platform and AI SaaS provider, offers several LLM families for enterprise use, including Command, Rerank, Embed, and Aya.
In brief, Command LLMs power tool-using agents, retrieval augmented generation (RAG), copywriting, and more. Rerank quickly adds LLM intelligence to existing search systems, while Embed improves search, classification, clustering, and RAG results. The Aya family expands multilingual and multimodal capabilities.
Thanks to their RAG capabilities, Cohere’s models are ideal for retrieval systems across a variety of applications. By grounding responses in external documents, they improve accuracy, reduce hallucinations, and even provide citations to support their answers.
Here are some tips on whether Cohere is a good choice for your needs.
Your business needs Cohere because it:
→ Offers robust data privacy and compliance features.
→ Works great for tasks like semantic search, document summarization, and knowledge retrieval.
→ Provides scalable models that can be fine-tuned to specific business needs.
→ Supports flexible deployment options, including SaaS, cloud API, and on-premises solutions.
But it would be wise to keep in mind that Cohere:
❗Might lack creative capabilities as most models are text-focused.
❗Is more suited for a business that has a dedicated data science or AI team, or is willing to partner with a third-party expert.
| Cohere pros & cons | |||
| ✔️ Enterprise-optimized performance | ✔️ Flexible deployment | ✔️ Customization | ✔️ Security |
| ❌ Limited creative capabilities | ❌ Requires tech expertise | ||
These days, there’s no shortage of popular large language models to pick from. But how do you know which one to choose? Let’s walk through the factors that matter.
Key factors for choosing the best LLM model
Picking the best LLM model for your project becomes easier once you know which aspects to focus on.
Integration with your existing technical ecosystem
When choosing the best LLM AI provider, consider how the model fits into your current tech setup. Some models offer easy-to-use APIs that you can plug right into your applications with minimal effort. Others are open-source and give you more control but require your team to handle deployment and maintenance.
We’ll help you figure out the right model for your needs and set it up.
Reach out and we'll handle itCosts and affordability
Many assume open-source large language models are free, but while there are no token fees, infrastructure costs depend on the model you choose.
Proprietary (API type) language models often outperform open-source options for tasks like generating human-like responses. This performance makes them worth the cost for most businesses. Monthly expenses vary by model and usage.
For instance, let’s compare GPT prices for input. GPT-5 costs $1.25/1M tokens and GPT-5 mini – $0.25/1M tokens. If you want to fine-tune a model like GPT-4.1, training costs rise to $25 per 1M tokens, plus fees for input, cache, and output tokens. On the low end, yearly costs typically range from $1,000 to $50,000, depending on usage and the model.
Scalability
Understanding how well a large language model can adapt and handle larger workloads as demand grows is crucial. That's where large language model operations (LLMOps) come in. LLMOps is basically a set of tools and methods used to make sure language models run smoothly and efficiently regardless of challenges like increased demand. For instance, Meta used LLMOps to create Code Llama.
Scalability can also be achieved by using pre-built models tailored to your specific industry. At Flyaps, for example, we have a variety of LLM-driven tools for recruitment, logistics, or fintech.
Data privacy and security
Large language models offer great potential, but data privacy is a growing concern. GPT, Claude, and Gemini might retain data longer than users expect, raising privacy issues. The industry is gradually shifting toward a user-first approach, so it's important to review the security settings of platforms offering these models.
There's no "best" LLM (and that's the point)
When clients ask us which large language model is the "best," we give them the same answer every time:there isn't one.
Each LLM comes with trade-offs, and what works depends on what you're trying to accomplish. The real question isn't "which is best?" but "which fits my specific needs?" A lightweight model might be perfect for search or mobile apps, while a cutting-edge multimodal model could be exactly what you need for enterprise integration.
In short, there is no universal champion among LLMs. Success comes from aligning the model’s strengths with the specific goals, constraints, and priorities of the project.
Final thoughts
Modern LLMs do more than text. They read images, listen to audio, and handle complex tasks. And who knows what OpenAI or Google will roll out tomorrow? Your mission is simple: pick the model that fits your goals, your budget, and your timeline. That’s how you find your best large language model.
Overwhelmed by all the technical details? We make it simple. Drop us a line, and we’ll guide you every step of your AI project.
We’ll analyze your goals and recommend the right fit.
Learn moreGot questions on the best LLMs?
What’s the difference between an open-source LLM and a proprietary LLM?
Open-source LLMs (like LLaMA or Falcon) allow developers to access and fine-tune the models, often running them on their own hardware. Proprietary LLMs (like GPT-4o or Gemini) are accessed via API and maintained by the provider. Open-source gives more control and privacy but requires technical expertise, while proprietary options are easier to deploy but may come with higher ongoing costs.
Can I train my own LLM from scratch?
Technically, yes, but it’s rarely practical. Training larger models requires enormous datasets, specialized hardware, and thousands of dollars in resources. Most businesses fine-tune popular LLM models or adapt proprietary APIs to meet their needs.
Are popular LLMs always the right choice for every project?
Not necessarily. The most popular LLMs are powerful, but for narrow use cases, simpler models or domain-specific solutions may be more cost-effective and easier to deploy.
Which industries benefit most from popular LLM models?
Popular LLM models are widely used in customer support, healthcare, finance, logistics, recruitment, marketing, and education, thanks to their versatility and adaptability. They power chatbots, streamline research, detect fraud, optimize supply chains, screen resumes, and generate content at scale. Beyond these, sectors such as law, energy, and manufacturing are also adopting the best large language models for automation and smarter decision-making.
Which LLM is the best?
There isn’t a single “best” large language model for every use case. The right choice depends on your needs. GPT-5 is one of the best language models for general-purpose tasks like reasoning, coding, and customer support. Gemini might be the best AI LLM if you need multimodal capabilities (text, images, audio, video). Claude 4 excels in coding and complex reasoning. Cohere is a strong fit for enterprise search and retrieval. Open-source models like LLaMA 4 and Falcon are the most popular large language models for businesses that want control, customization, and on-premises deployment.
Bonus tip: Pay attention to the model’s context window, which determines how much text it can “see” and reason over at once.






